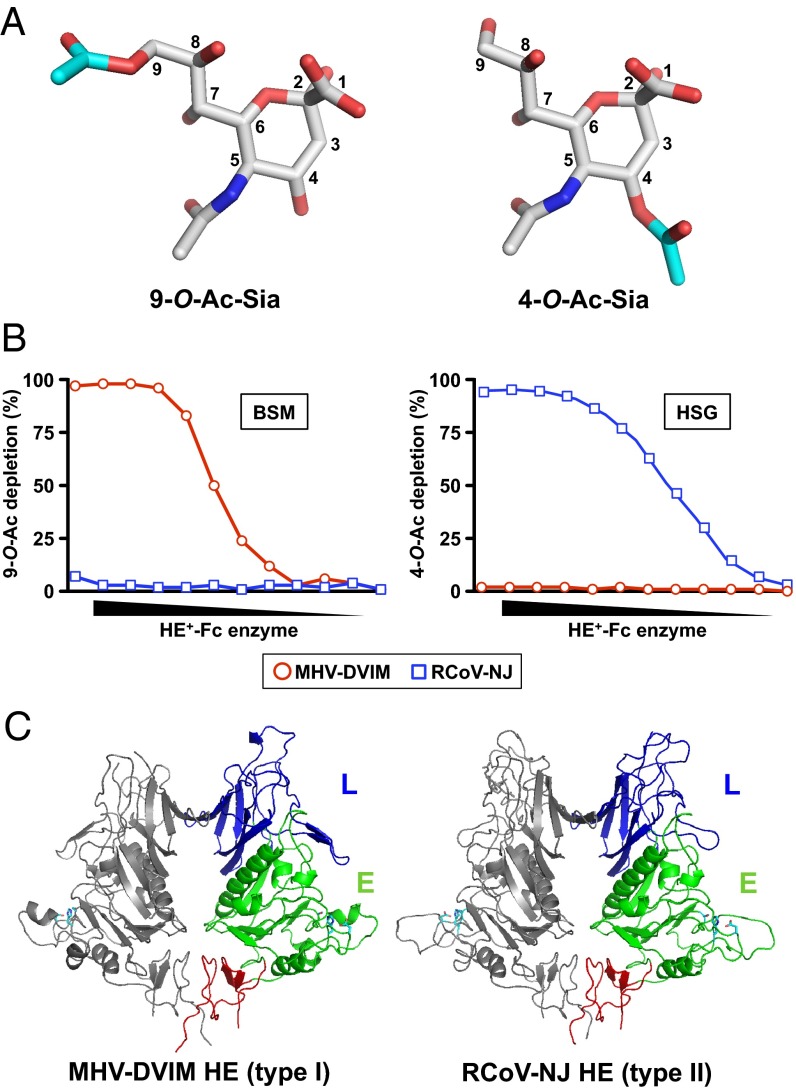
Fig. 1.
(A) Stick representation of 9-O-Ac-Sia and 4-O-Ac-Sia. O-Ac moieties are depicted with carbon atoms in cyan. (B) Substrate specificity of MHV-DVIM HE (red circles) and RCoV-NJ HE (blue squares). BSM (Left) and HSG (Right) were coated in MaxiSorb plates and incubated with twofold serial dilutions (starting at 100 ng/µL) of enzymatically active HE-Fc fusion proteins. Loss of 4-O- and 9-O-Ac-Sias (indicated by percentual depletion on the y axis) was assessed by solid-phase lectin-binding assay with enzymatically inactive virolectins MHV-S HE0-Fc and PToV-P4 HE0-Fc, respectively, with virolectin concentrations fixed at 50% maximal binding. (C) Cartoon representation of the crystal structures of the RCoV-NJ HE and MHV-DVIM HE dimers. The Left monomer is colored gray, the other by domain: lectin domain (L, blue); esterase domain (E, green) with Ser-His-Asp active site triad (cyan sticks); membrane proximal domain (red).