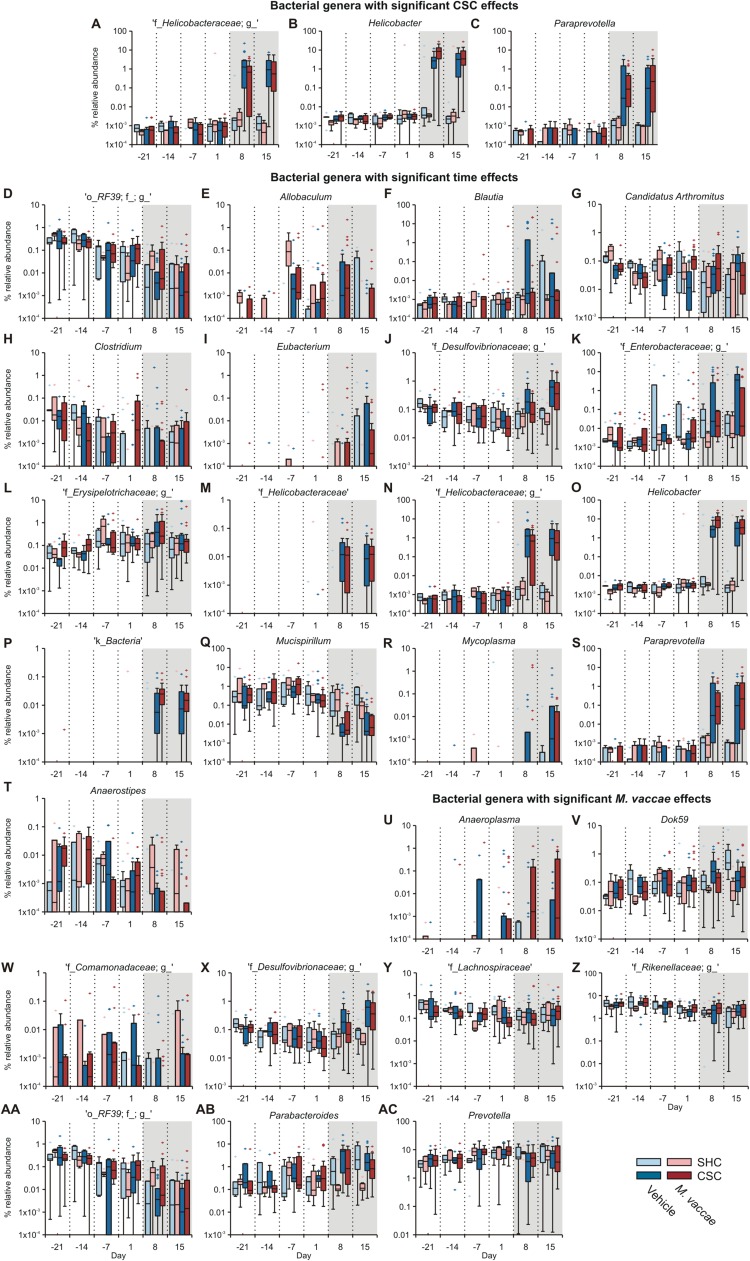
Fig. S5.
Gut microbiota data of Exp. 1, showing main effects of M. vaccae, CSC, and time on gut microbial composition. (A–C) Main effects of CSC on gut microbial composition. Main effects of CSC exposure, relative to SHC, were analyzed separately on days 8 and 15 using ANCOM (significant at FDR 0.05). Main effects of CSC, relative to SHC controls, were observed for the following genera. (A) An unidentified genus within the Helicobacteraceae family on days 8 and 15. (B) Helicobacter on days 8 and 15. (C) Paraprevotella (Bacteroidetes) on day 15. Gray shading indicates the onset of the CSC procedure immediately following collection of fecal samples on day 1. (D–T) Effects of time, within specific treatment groups, on gut microbial composition. Box plots illustrate main effects of time, based on analysis of all six time points, using ANCOM (significant at FDR 0.05). For significant post hoc comparisons, based on Wilcoxon signed-rank tests comparing day 1 with day 8 and day 1 with day 15, see Table S3. Effects of time were observed for the following genera. (D) An unidentified genus in the order RF39 (Tenericutes; vehicle/SHC, M. vaccae/SHC, M. vaccae/CSC). (E) Allobaculum (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC). (F) Blautia (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC). (G) Candidatus Arthromitus (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC). (H) Clostridium (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC). (I) [Eubacterium] (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (J) An unidentified genus in the family Desulfovibrionaceae (Proteobacteria; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (K) An unidentified genus in the family Enterobacteraceae (Proteobacteria; vehicle/CSC). (L) An unidentified genus in the family Erysipelotrichaceae (Firmicutes; vehicle/CSC). (M) An unidentified genus in the family Helicobacteraceae (Proteobacteria; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (N) A second unidentified genus in the family Helicobacteraceae (Proteobacteria; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (O) Helicobacter (Proteobacteria; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (P) An unidentified genus in the kingdom Bacteria (vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (Q) Mucispirillum (Deferribacteres; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (R) Mycoplasma (Tenericutes; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (S) Paraprevotella (Bacteroidetes; vehicle/CSC, M. vaccae/CSC). (T) Anaerostipes (Firmicutes; M. vaccae/CSC). Gray shading indicates the onset of the CSC procedure immediately following collection of fecal samples on day 1. (U–AC) Main effects of immunization with M. vaccae, relative to immunization with vehicle, were analyzed separately on days 8 and 15 using ANCOM (significant at FDR 0.05). We observed a main effect of M. vaccae to stabilize the abundance of several genera on day 8 and/or 15, including Dok59, an unidentified genus of Desulfovibrionaceae, and Parabacteroides. Main effects of M. vaccae, relative to vehicle, were observed for the following genera. (U) Anaeroplasma (Tenericutes) on day 8. (V) Dok59 (Proteobacteria) on day 8. (W) An unidentified genus in the family Comamonadaceae (Proteobacteria) on day 8. (X) An unidentified genus in the family Desulfovibrionaceae (Proteobacteria) on day 8. (Y) An unidentified genus in the family Lachnospiraceae (Firmicutes) on day 8. (Z) An unidentified genus in the family Rikkenellaceae (Bacteroidetes) on day 8. (AA) An unidentified genus in the order RF39 (Tenericutes) on day 8. (AB) Parabacteroides (Bacteroidetes) on days 8 and 15. (AC) Prevotella (Bacteroidetes) on day 8. Gray shading indicates the onset of the CSC procedure immediately following collection of fecal samples on day 1. Data are expressed as percent relative abundance, which is the normalized proportion of genera counts, on a log scale. The bottoms and tops of boxes indicate the first and third quartiles, respectively; whiskers indicate 1.5 IQR beyond the upper and lower quartiles. Values outside the whiskers are indicated by +. The number of independent data points (N) in each of the graphs and sample size (n) for each group are as follows: N = 62; vehicle/SHC, 10; vehicle/CSC, 21; M. vaccae/SHC, 9; M. vaccae/CSC, 22.