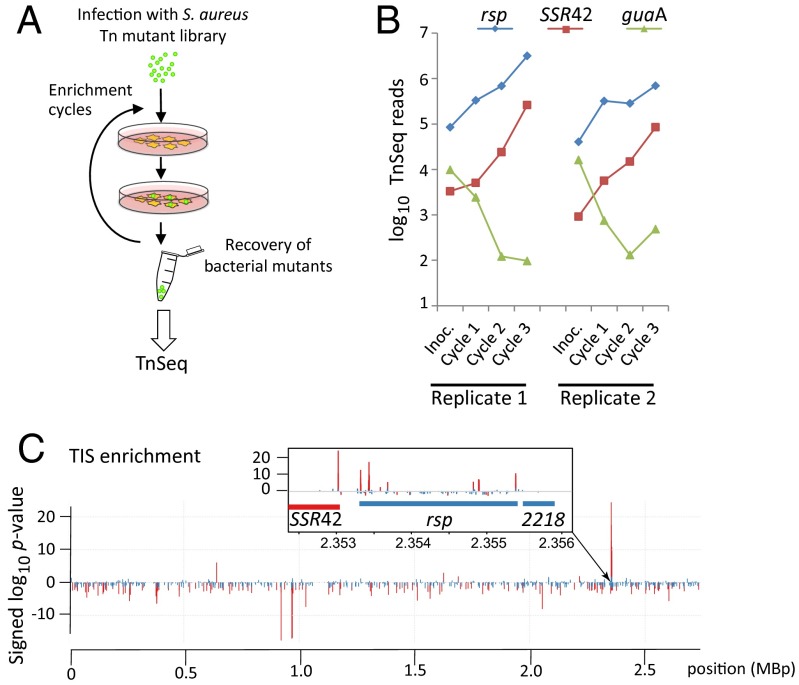
Fig. 1.
A genome-wide screen for noncytotoxic S. aureus identifies rsp and SSR42. (A) HeLa cells were infected with a mariner transposon mutant library of S. aureus 6850. Viable bacteria were recovered from host cells 8 h after infection and were used to reinfect epithelial cells in three consecutive enrichment cycles. Pools of recovered bacteria and the respective inoculum were analyzed by TnSeq. (B) Sequence reads from transposons within the genes encoding rsp (blue) and SSR42 (red) were strongly enriched in noncytotoxic mutants (P < 0.001). By contrast, transposon insertions in genes such as the drug target guaA (75) (green) were significantly depleted. (C) Genome-wide significance (signed log10 P values) of changes in TIS frequencies demonstrate that the locus encoding rsp and SSR42 is most significantly enriched (Inset). Positive and negative values on y axis, respectively, indicate enrichment and depletion in TIS reads compared with the inoculum. Significant changes (adjusted P < 0.05) are highlighted in red.