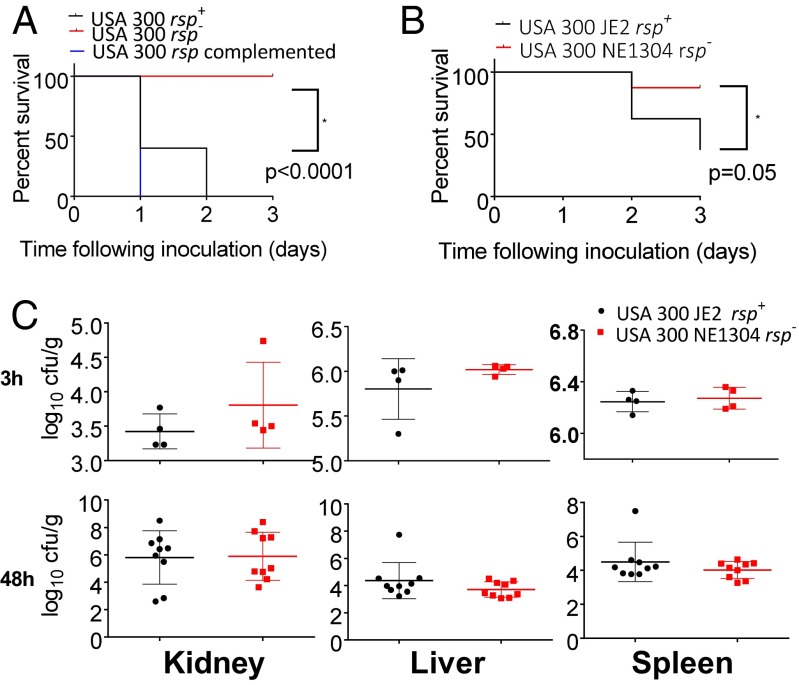
Fig. 3.
rsp mutants exhibit reduced lethality in mouse models but are capable of forming deep abscesses. (A) In a murine pneumonia model, infected mice survived when challenged with lethal doses of rsp mutants of strain USA300 LAC*, whereas wild-type and complemented strains were virulent (n = 10). The comparison shown is by log-rank test between wild-type and rsp mutant organisms. (B) In intravenous infections, mice were challenged with S. aureus USA300 JE2 or its rsp mutant. Significantly enhanced lethality was seen in the wild-type relative to the mutant. (C) Bacterial counts in kidney, liver, and spleen were comparable 3 and 48 h after intravenous infection. Shown is the number of colony-forming units (cfu) per gram of tissue.