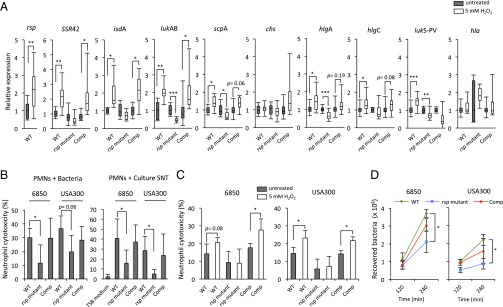
Fig. 7.
rsp effects are induced by hydrogen peroxide and regulate cytotoxicity toward PMNs. (A) Upon 10-min exposure to 5 mM hydrogen peroxide, transcription of rsp and its targets is up-regulated in exponentially growing wild-type S. aureus LAC* (WT). This response to hydrogen peroxide was rsp-dependent and rescued in complemented mutants (Comp). Values indicate expression levels of peroxide-challenged bacteria (open bars) relative to untreated controls (filled bars). Statistical analysis was performed by pairwise t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (B) Bacterial infection of PMN with wild-type, rsp mutant, and complementants, as well as treatment with bacterial culture supernatant for 4 h, demonstrated that host cell death levels were significantly decreased and complementable in rsp mutants. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) S. aureus culture supernatants collected from wild type, rsp mutant, and complementants after peroxide challenge exhibit increased cytotoxic potential in an Rsp-dependent manner. Human PMNs were intoxicated with the supernatants, and cytotoxicity was determined by LDH release. The vertical axis indicates the percentage of neutrophil cell death compared with complete cell lysis (positive control). Statistical analysis was performed by pairwise t test. *P < 0.05. (D) S. aureus (strains 6850 and USA300) rsp wild-type (WT), rsp mutant, and complementants (Comp) were used to infect neutrophils. Intracellular bacteria were recovered 2 and 4 h after infection, and number of viable bacteria was determined. Statistical analysis at each time point was performed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05 (rsp mutant compared with wild type).