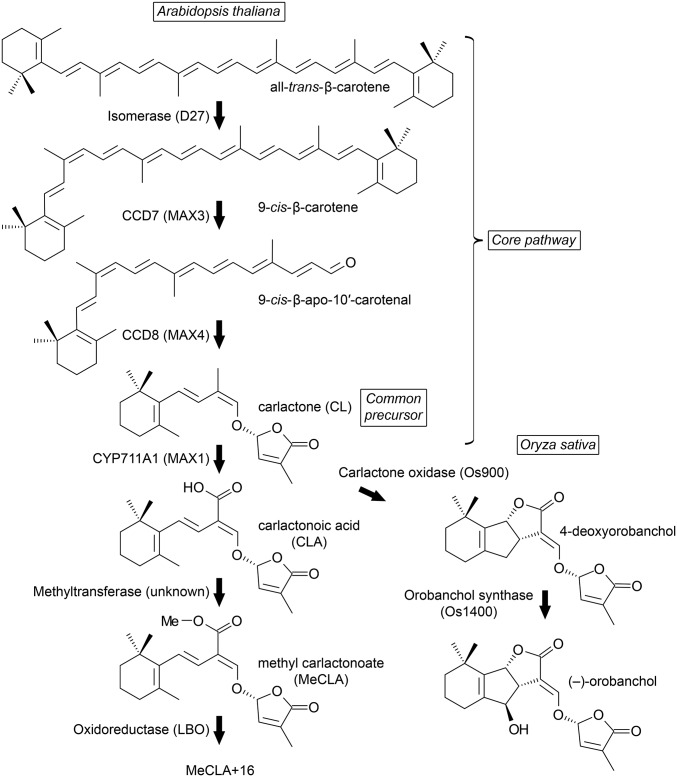
Fig. 1.
The strigolactone biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. An isomerase and two CCD enzymes convert β-carotene into CL, the common precursor of diverse strigolactones. In rice, CL is oxidized by two cytochrome P450 enzymes to orobanchol, which functions in the rhizosphere as a signal for mycorrhizal fungi. In Arabidopsis, CL is oxidized by the MAX1 cytochrome P450 to CLA, which is converted to MeCLA. Evidence presented in this study suggests that LBO facilitates additional processing to an unknown strigolactone-like product (MeCLA + 16 Da), which is required for the control of shoot branching.