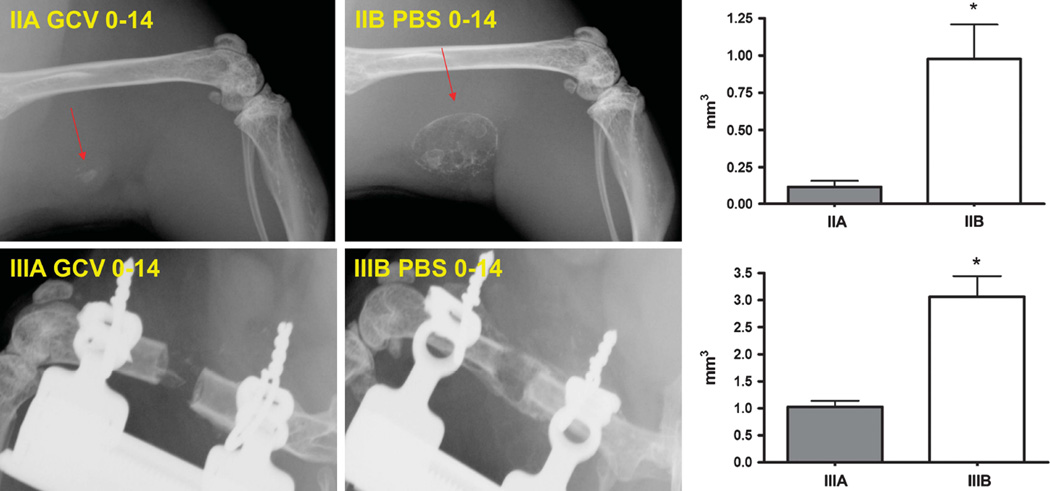
Figure 6.
Comparison of in vivo BMP-2 production in GCV-treated and control animals that received GCV or PBS injections from 0 to 14 days after surgery. A total of 2 × 106 LV-Δtk-T2A-BMP-2 transduced MBMCs were implanted in the muscle pouch or the 2-mm defects. Top panel (group IIA and IIB) shows the X-rays obtained at 4 weeks postoperatively in the muscle pouch model, and bottom panel (groups IIIA and IIIB) shows that obtained at 4 weeks postoperatively of the femoral defect models. Early GCV treatment resulted in significant inhibition of bone formation and lack of defect healing. Arrows point to the bony mass formed in the muscle pouch. µ-CT-based new bone volumes of the final specimens at 4 weeks show significant reductions in bone formation as a result of GCV treatment. Data expressed as mean ± s.e., n = 3 animals per group, *P < 0.05 compared with the experimental group.