Fig. 5.
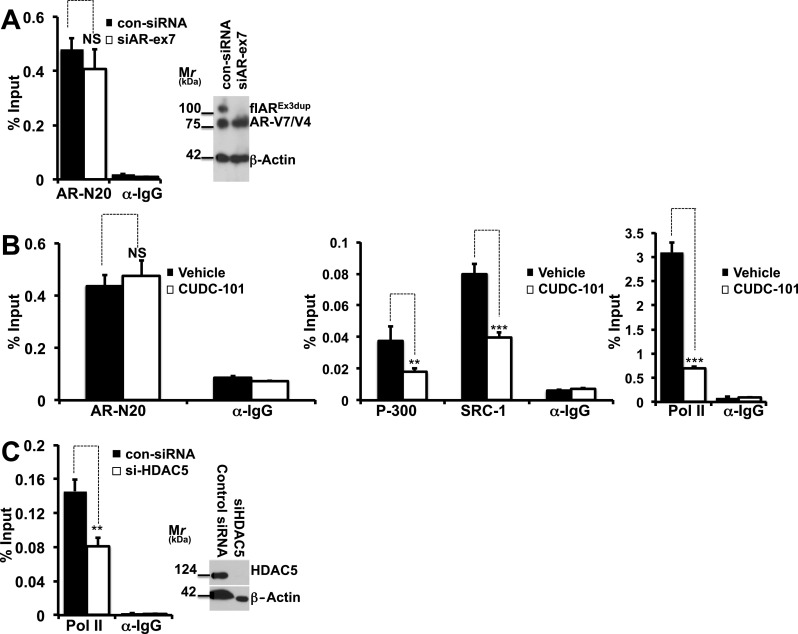
a–c CUDC-101 treatment or HDAC5 silencing prevent formation of an active AR-V7-dependent transcriptional complex at the level of the PSA enhancer. a 22Rv1 cells underwent experimental manipulation with specific siRNA’s to silence flAR or with control siRNA’s. Cells were grown in CS-FBS for 24 h, harvested and used for ChIP analysis performed with anti AR Ab-N20 (Santa Cruz) or rabbit IgG. Right panel Immunoblot analysis for flAR, AR-V7 and beta actin. Left panel ChIP analysis measuring AR-V7 bound to PSA promoter. NS: denotes statistically non-significant difference when comparing 22Rv1 cells with silenced flAR (siAR-ex7) to control cells (con-siRNA). b 22Rv1 cells were starved in CS-FBS medium. After 24 h cells were treated for 6 h with CUDC101 at the concentrations of 300 nM and harvested. AR, P-300, SRC-1 and RNA pol II binding to the PSA enhancer was measured by ChIP followed by qPCR using AR, RNA polymerase II, p300, SRC-1, and rabbit and mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies (all from Santa Cruz). NS: statistically non-significant; **P > 0.01, ***P > 0.001 compared to vehicle treated cells. c 22Rv1 cells underwent experimental manipulation with specific siRNA’s to silence HDAC5 or with control siRNA’s. Cells were grown in CS-FBS for 24 h and harvested. RNA pol II bound to the PSA enhancer was measured by ChIP followed by qPCR (left panel) using anti Pol II or rabbit IgG antibodies. Right panel Immunoblot analysis for HDAC5 and beta actin demonstrating silencing of HDAC5. **P < 0.01 when comparing 22Rv1 cells with silenced HDAC5 (si-HDAC5) to control cells (con-siRNA)
