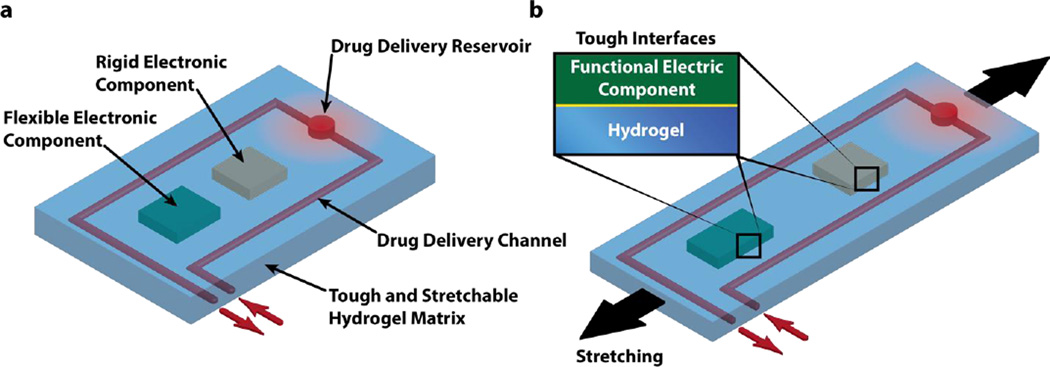
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the design of stretchable hydrogel electronics and devices.
a) Functional electronic components such as conductors, microchips, transducers, resistors, and capacitors are embedded inside or attached on the surface of the hydrogel. Drug-delivery channels and reservoirs are patterned in the hydrogel matrix, and they can diffuse drugs out of the hydrogel to give programmable and sustained release of drugs. b) As the hydrogel electronic device is stretched, flexible electronic components can deform together with the device but rigid components will maintain their undeformed shapes, which requires robust interfaces between electronic components and hydrogel matrix.