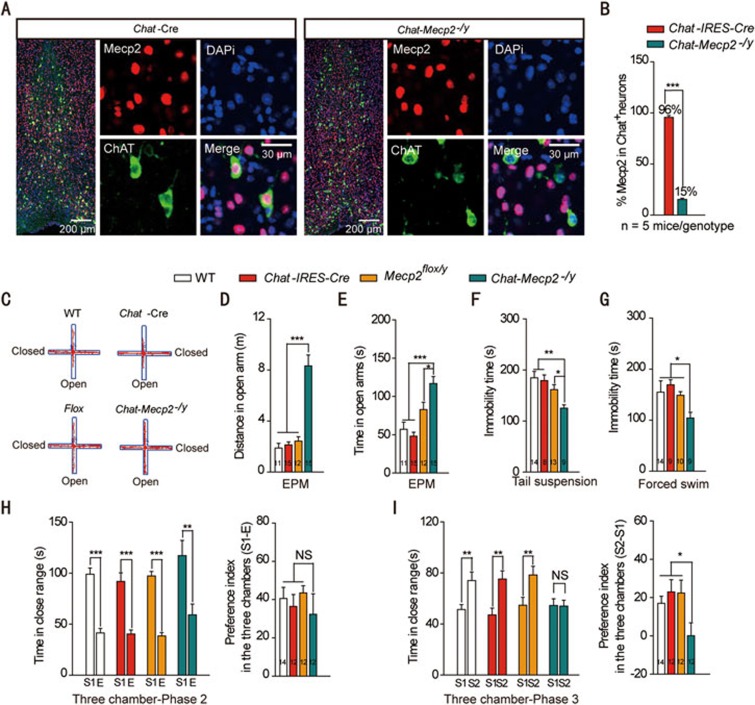
Figure 1.
Chat-Mecp2−/y mice lost MeCP2 in cholinergic neurons and developed part of RTT-like phenotypes. (A) Fluorescence images showing BF sections stained for the nucleus (DAPI), MeCP2 and ChAT. (B) Percentage of MeCP2 immunostaining cells in BF cholinergic neurons in Chat-IRES-Cre and Chat-Mecp2−/y mice (two-sided t-test). (C-E) Anxiety-related behavior examined by the elevated plus-maze. Data are distance and time that Chat-IRES-Cre and Chat-Mecp2−/y mice spent in the open arms of the EPM. P-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison. (F, G) Depression-related behavior measured by the immobility time that Chat-IRES-Cre and Chat-Mecp2−/y mice displayed in the tail suspension and forced swim tests. P-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA with T Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison. (H, I) Social behavior examined in the three-chamber test. (H) Left: In the second phase of the three-chamber test, mice of each genotype spent more time on interacting with the stranger mouse than the empty cage. P-values were calculated by two-sided t-test. Right: Data are ratios of interaction time with a stranger mouse to interaction time with an empty cage. One-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison was used. (I) Left, In the third phase, control mice spent more time on interacting with the unfamiliar stranger, and Chat-Mecp2−/y mice had no preference for either cage. P-values were calculated by two-sided t-test. Right: Data are ratios of interaction time with a stranger mouse to interaction time with a familiar mouse. One-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison was used. Error bars are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.