Figure 1. Correlation of Asp racemization ratio with subject age for OA whole cartilage and extracted matrix components.
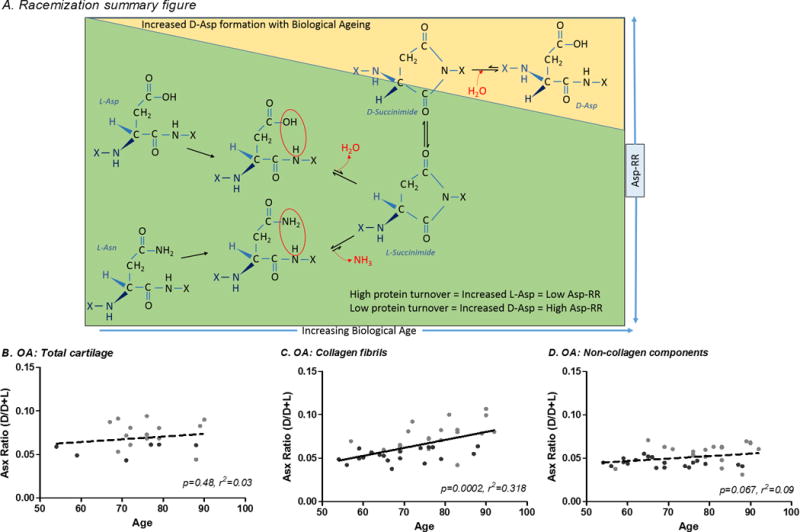
(A) Process of Asp racemization through a succinimide intermediate. Asp racemization ratio (Asp-RR=D-Asp/D+L Asp) was determined for OA cartilage including: (B) whole cartilage (full thickness macroscopically normal cartilage), (C) collagen fibrils (cartilage extensively extracted with Gu-HCl to remove soluble cartilage proteins leaving mainly collagen) and, (D) non-collagen cartilage components (proteins extractable from cartilage by Gu-HCl, mainly aggrecan). Briefly, Hydrolysates were buffered with 0.4M boric acid (pH9.0) and derivatized with o-phthaldialdehyde and N-tertiarybutyloxycarbonyl-L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) in methanol. Resulting fluorescent derivatives were separated by reverse-phase HPLC. A total of 100μl of derivatized sample was injected onto a Chromolith RP-18e 100×4.6mm column (VWR International LLC, USA) at a 1ml/min flow rate with fluorescent detection (excitation 344nm, emission 443nm) using the following gradient: 30min 9.5–15.5% buffer B (100% acetonitrile); 5min 60% buffer B column wash. Mobile phase consisted of 0.2M acetic acid adjusted to pH6.0 with NaOH. The Asp racemization ratio (Asp-RR) was defined as D/D+L Asp.
