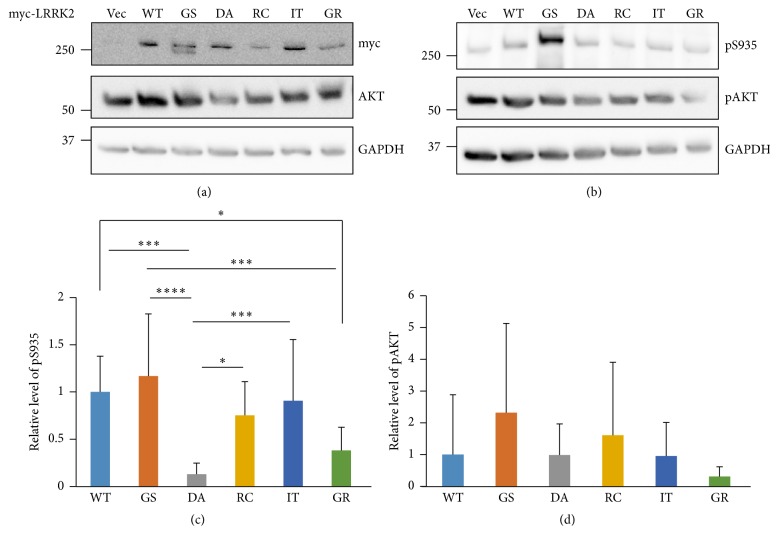
Figure 3.
Kinase activities of cellular LRRK2 proteins. HEK 293T cell lysates transiently expressing the indicated myc-tagged LRRK2 WT and mutant proteins were separately loaded onto two gels and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The membranes were cut to a proper size to detect the corresponding proteins. Myc-tagged LRRK2 and AKT1 were detected by myc and AKT antibodies, respectively ((a): myc and AKT). LRRK2 kinase activities are shown as autophosphorylation of LRRK2 (detected by pS935 antibody, (b): pS935) and phosphorylation of the AKT LRRK2 substrate ((b): pAKT). GAPDH was used as a loading control. A representative of 12 different experiments is shown (a and b). Relative kinase activities of autophosphorylated LRRK2 (c) and phospho-AKT (d) after a statistical analysis were also shown. Relative pS935 or pAKT levels were calculated by dividing the GAPDH value by that for the phosphorylated proteins, which was again divided by total LRRK2 or AKT, respectively. The resulting pAKT number was divided by total LRRK2 (myc) to consider equal quantities of the LRRK2 kinase and substrates (d). All values are relative to the WT and are expressed as the mean ± SD. Vec: empty vector, WT: wild type, GS: G2019S, DA: D1994A, RC: R1441C, IT: I2020T, and GR: G2385R. ∗ p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗∗ p ≤ 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗ p ≤ 0.0001.