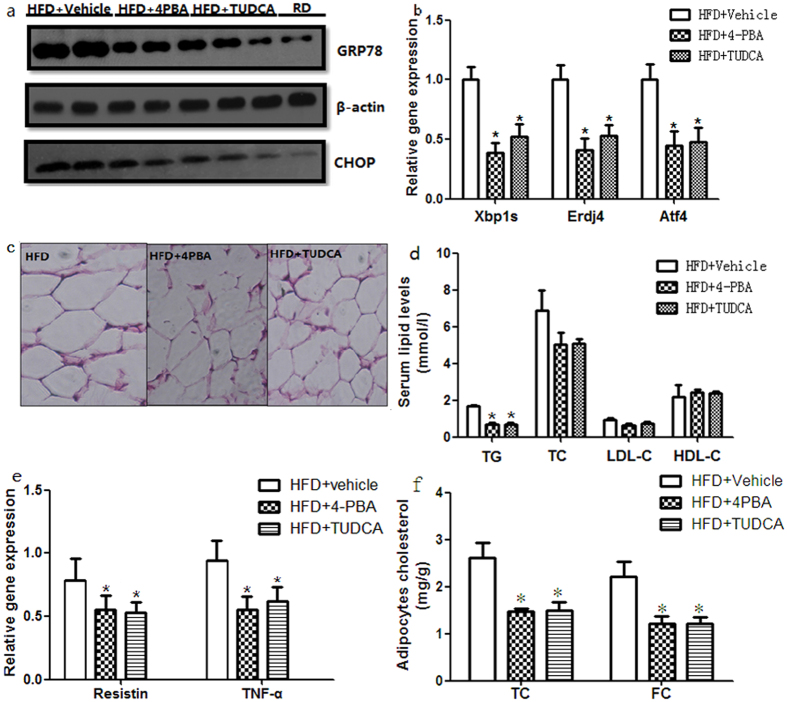
Figure 2. Chemical chaperones modify ER stress and inflammatory in mice fed a high-fat diet.
Mice were fed a high-fat diet for 14 weeks and then treated with 4-PBA or TUDCA for 6 weeks at a dose of 1 g/kg/day. (a) Protein expression levels of ER stress markers in adipose tissue. Protein expression levels of ER stress markers were significantly depressed by treatment with 4-PBA or TUDCA. Values are means ± SD (n = 10). (b) Gene expression of UPR markers indicating the state of ER stress pathways in adipose tissue. The gene expression of Xbp1s, Erdj4 and Atf4 were also decreased by 4-PBA or TUDCA. Values are means ± SD (n = 10). (c) H&E staining of adipose tissue. Treatment with 4-PBA or TUDCA slightly decreased the size of the adipocytes. (d) Effects of 4-PBA or TUDCA on serum lipids and glucose concentrations of mice fed a high-fat diet. The blood glucose and triglyceride levels of obese mice treated with 4-PBA (n = 10) or TUDCA (n = 10) were significantly lower than those of vehicle-treated obese mice (n = 10). Serum TC and LDL-C had a slight but not significant decrease by the treatment of chemical chaperons. (e) Gene expression levels of inflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue. The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines were down-regulated by treatment with 4-PBA or TUDCA. (f) TC and FC in adipocytes form mouse epididymal adipose tissue after treatment of 4-PBA or TUDCA. Both the adipocytes TC and FC were decreased by the treatment of chemical chaperones (n = 10). Values are means ± SD. *p < 0.05 (compared with HFD + vehicle group).