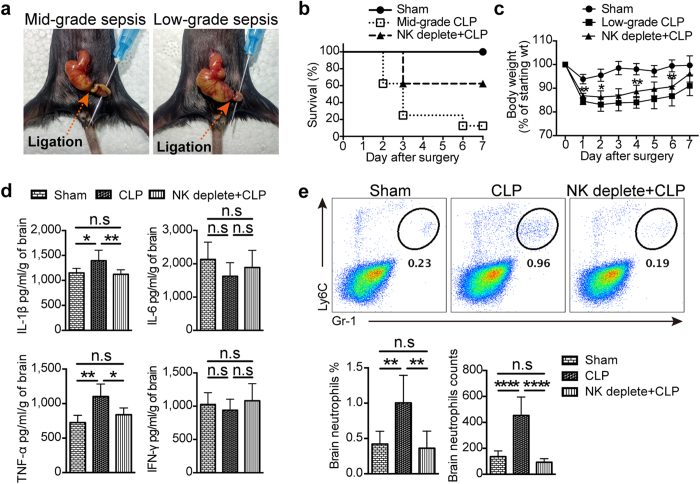
Figure 6. NK cells regulate neutrophil recruitment in the brain during CLP-induced neuroinflammation.
(a) Two CLP models with different severity were prepared. For mid-grade CLP, 50% of the cecum was ligated; For low-grade CLP, 25% of the cecum was ligated. (b) Survival rate in sham group, mid-grade CLP group with or without NK cell depletion (n = 8, per group) was detected in 7 days after surgery. (c) The body weight of mice (n = 8 per group) in 7 days after surgery was measured in mice with low-grade CLP. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t test, when compared with low-grade CLP group. Means ± SD are shown. (d) Three days after surgery, proteins were extracted from the whole brain of mice in sham group, low-grade CLP group with or without NK cell depletion (n = 6 per group). ELISA was performed to detect the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines in the brain. (e) Three days after surgery, prepared single cell suspensions from the whole brain in low-grade CLP group and control group (n = 5 per group) were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry. Histogram shows the percentage and cell number of CD45+Gr-1hiLy6C+ neutrophils. (c–e) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ANOVA. Means ± SD are shown. All data in this figure are representative of at least 2 independent experiments.