Figure 1.
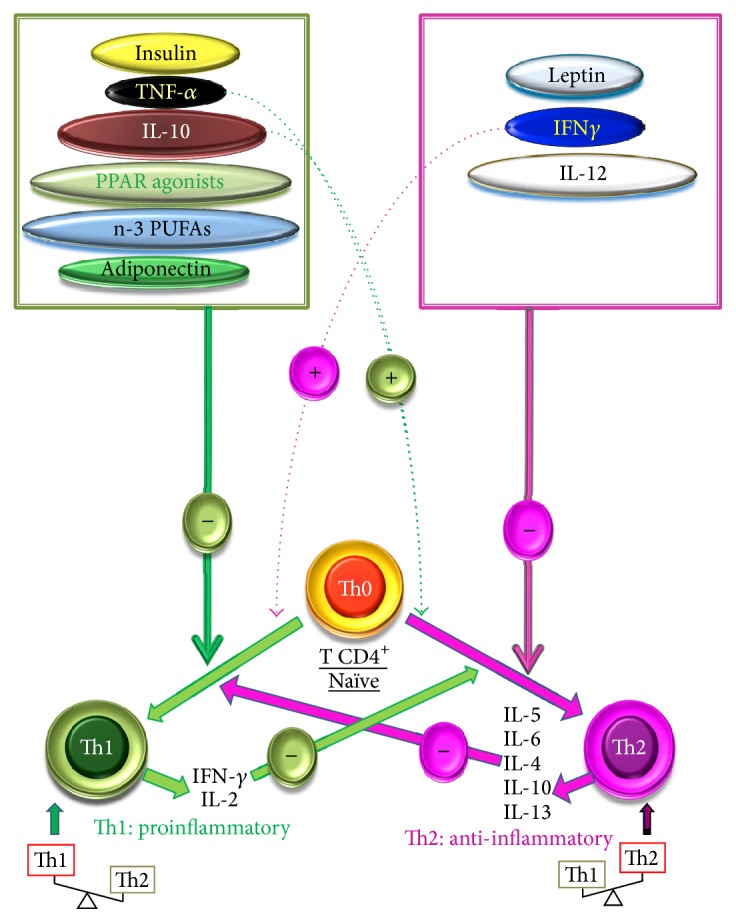
Differentiation of Th0 cells into Th1 and Th2 cells and their modulation. The secretion of their respective cytokines identifies the cells. Th0 cells, which principally secrete IL-2 along with other some cytokines, are differentiated either into Th1, under the action of IL-12 and IFN-γ, released by the macrophages and NK cells (natural killer), respectively, or into Th2 phenotype by the action of IL-4 produced by the mastocytes. The IFN-γ and IL-10 exert an inhibitory effect on the differentiation of Th1 and Th2 phenotypes, respectively. Insulin, PPAR agonists, and n-3 PUFAs promote the differentiation into Th2 phenotype. Leptin promotes the differentiation into Th1 cells. (+) inducing effect; (−) inhibitory effect.
