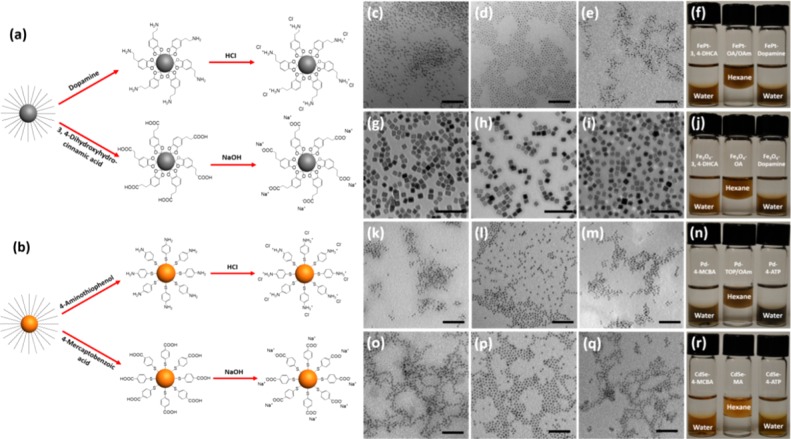
Figure 1.
Ionization of hydrophobic colloidal nanoparticles. (a) Schematic representation of ionization of alloy metal (FePt) and metal oxide (Fe3O4) NPs with dopamine and 3,4-DHCA. (b) Schematic representation of ionization of noble metal (Pd) NPs and quantum dots (CdSe) with 4-ATP and 4-MCBA. TEM images of (c) ionic FePt, (g) cubic Fe3O4, (k) Pd, and (o) CdSe nanoparticles with 3,4-DHCA and 4-MCBA in water, respectively. TEM images of (d) FePt, (h) cubic Fe3O4, (l) Pd, and (p) CdSe nanoparticles in hexane. TEM images of (e) ionic FePt, (i) cubic Fe3O4, (m) Pd, and (q) CdSe nanoparticles with dopamine and 4-ATP in water, respectively. Corresponding photographic images of (f) FePt, (j) cubic Fe3O4, (n) Pd, and (r) CdSe nanoparticles in hexane and water after ligand exchange and ionization. Scale bar: FePt, Pd, and CdSe are 50 nm. Cubic Fe3O4 is 100 nm.