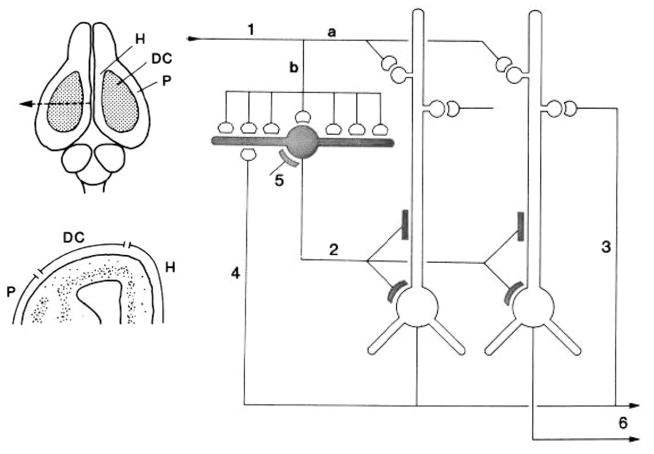
Fig. 13.
Left, above: Dorsal view of the brain of the turtle Pseudemys scripta. Abbreviations: DC, dorsal cortex; H, hippocampus; P, pyriform (olfactory) cortex. Below, cross-section of the forebrain at the level of the arrow in top diagram, showing the relative positions of pyriform (P), hippocampal (H), and dorsal cortex (DC). From Connors and Kriegstein (1986). Right: Summary of the microcircuit organization of turtle dorsal cortex. Thalamocortical afferent volleys (1) excite pyramidal cell dendrites (a) and also inhibitory stellate cells (b). Stellate cell-pyramidal cell contact (2) mediates feedforward inhibition. Pyramidal cell output mediates reciprocal excitation between pyramidal cells (3) as well as feedback inhibition (4). Stellate-stellate cell contacts mediate inhibition (5). The pyramidal cell axons provide output (6) After Kriegstein and Connors (1986). Open profiles: excitatory synaptic action; filled profiles: inhibitory synaptic action.