Fig. 11.
PSD enzyme inhibition and in vivo efficacy of 7CPQA.
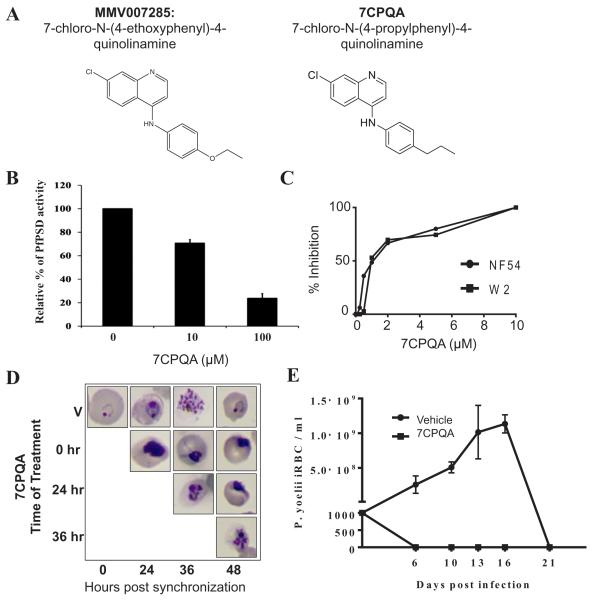
A. Chemical structures of MMV007285 and 7CPQA.
B. In vitro inhibition of PfPSD by 7CPQA. MBP-PfPSDΔ40 was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 codon plus strain and purified by amylose column affinity chromatography. PSD enzyme analysis was performed with the purified enzyme in the presence of DMSO alone, 10 μM or 100 μM of 7CPQA for 45 min at 30°C as described in Experimental Procedures. PSD activity of 7CPQA-treated MBP-PfPSDΔ40 was normalized to 100% of MBP-PfPSDΔ40 treated with DMSO control. Data are means ± standard deviation for three experiments each performed in duplicate.
C. Inhibition of NF54 (closed circles) and W2 (closed squares) parasite clones as a function of CPQA concentrations. Values are means of triplicates.
D. Stage specific inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum (NF54) parasite by 7CPQA. Highly synchronized cultures of the parasites were grown in the absence or presence of 10 μM of 7CPQA, stained by Giemsa stain, and analyzed by light microscopy.
E. In vivo efficacy of 7CPQA against Plasmodium yoelii XNL strain. Two groups of 6-week-old female Swiss Webster mice were injected with 103 infected red blood cells. On days 4, 5 and 6 after infection, three mice were administered a single daily dose of vehicle alone (PEG-400) and four mice were administered vehicle containing 30 mg kg−1 of 7CPQA by oral gavage. Parasitemia was monitored by collecting blood from animals and determining the number of infected red blood cells by Giemsa staining (counting at least 5000 red blood cells).