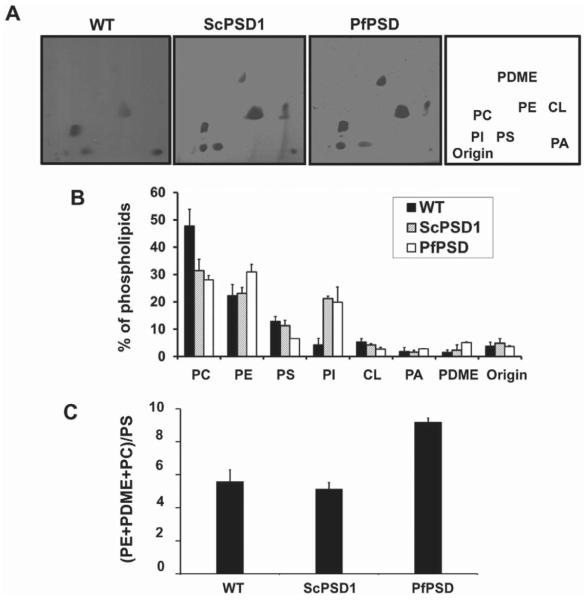
Fig. 3.
Phospholipid composition of wild-type yeast and mutant strains expressing only yeast or parasite PfPSD. The WT strain (BY4741-pVUT-102U)), and a Δpsd2Δdpl1Δ strain harboring yeast PSD1 (ScPSD1), and the psd1Δpsd2Δdpl1Δ mutant strain harboring pBEVY-PfPSD (PfPSD were grown to log phase in synthetic uracil dropout medium, and lipids were extracted and separated by two-dimensional TLC.
A. The lipids were visualized by iodine staining.
B. The isolated lipids were quantified by phosphorus analysis and the results are expressed as the percentage of total lipid phosphorus. Data are expressed as mean ± range of two experiments.
C. The ratio of product, PE + PDME + PC, over precursor, PS, is indicative of PSD function in vivo. Abbreviations: PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PS, phosphatidylserine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; CL, cardiolipin; PA, phosphatidic acid, PDME, phosphatidyldimethylethanolamine.