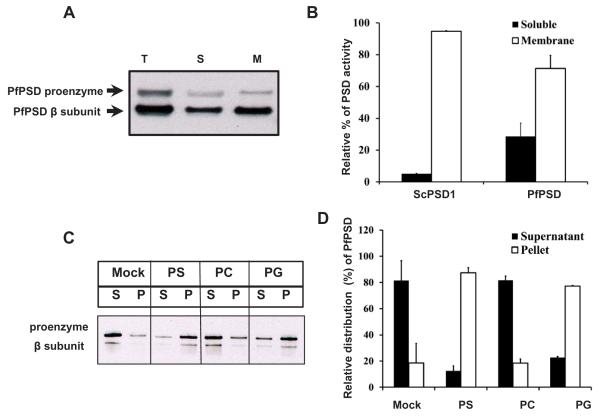
Fig. 4.
Biochemical properties of heterologously expressed PfPSD.
A. Western blot analysis was performed with rabbit anti-PfPSD antibody and HRP conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody to detect PfPSD in the psd1Δpsd2Δdpl1Δ mutant strain expressing PfPSD. Total cell free extracts (T), soluble fractions (S), and membrane fractions (M) were analyzed using anti-PfPSD. The upper band and the lower band are the PfPSD proenzyme and the mature β-subunit, respectively.
B. PSD enzyme assays were performed with soluble fractions and membrane fractions extracted from yeast psd1Δpsd2Δdpl1Δ mutant strains expressing PfPSD. Measurement of PSD catalytic activity utilized Ptd[1′-14C]Ser as the substrate, and the reaction product was trapped as 14CO2 on 2 M KOH impregnated filter paper. Data are means ± standard deviation for two experiments each performed in duplicate.
C. An MBP-PfPSD fusion protein was expressed in Escherichia coli and affinity purified using amylose resin. The binding of MBP-PfPSD to phospholipids was measured after incubation at 37°C for 40 min, using co-sedimentation of the enzyme with multilamellar liposomes (200 μg ml−1) centrifuged at 10,000 × g × 5 min. Aliquots of the supernatant (S) were taken for gel electrophoresis and Western blotting. The resultant pellets were collected and diluted to the same volume as the supernatants, and analyzed by electrophoresis and Western blotting. Mock, indicates no incubation of extracts with liposomes and PS, PC and PG indicate the lipid classes used in separate incubations.
D. Quantification of the enzyme distribution data from panel C. The protein band intensities of the proenzymes and processed β-subunits of the supernatant and the liposome pellet on the Western blot were quantified using Image J software. Data are means ± range for two experiments.