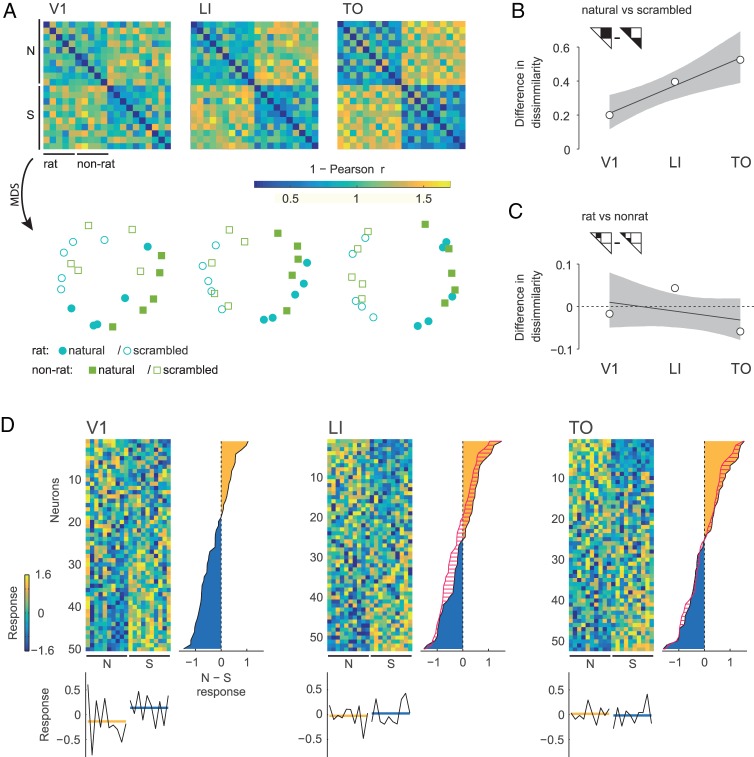
Figure 4.
Stimulus representations based on responses averaged across movie durations. Panel A shows the stimulus dissimilarity matrices based on the correlation distance for each population of neurons recorded in V1, LI, and TO (upper row). Nonmetric MDS is then used to represent the representational space in 2 dimensions (lower row). Panel B shows the difference between dissimilarities for stimulus pairs of the opposite stimulus type (i.e., natural versus scrambled) and dissimilarities for pairs of the same type in areas V1, LI, and TO. Gray area indicates 95% confidence bounds for OLS regression, calculated by BCa. Panel C is the same as panel B, but for the difference between dissimilarities for stimulus pairs of the opposite stimulus category (i.e., rat versus nonrat) and dissimilarities for pairs of the same category. Panel D contains heatmaps (one per area) displaying the average response to each movie standardized per neuron (Z-score across stimuli). Neurons (rows) are sorted in descending order according to the values of the average standardized response to natural movies minus that to their scrambled versions. To the right of each heatmap the average of this value used for sorting is plotted per neuron, with the yellow area indicating neurons that respond more to natural images than to their scrambled version and the blue area indicating the reverse. For LI and TO, red hatching indicates how this distribution changed from V1 and LI respectively. Stimuli (columns) are sorted in the same way as in the dissimilarity matrices: 5 natural rat movies, 5 natural nonrat movies, and their scrambled versions in the same order. Column averages are displayed below each heatmap (black lines), with the average across stimulus type (yellow for natural movies, blue for their scrambled version) indicated in color.