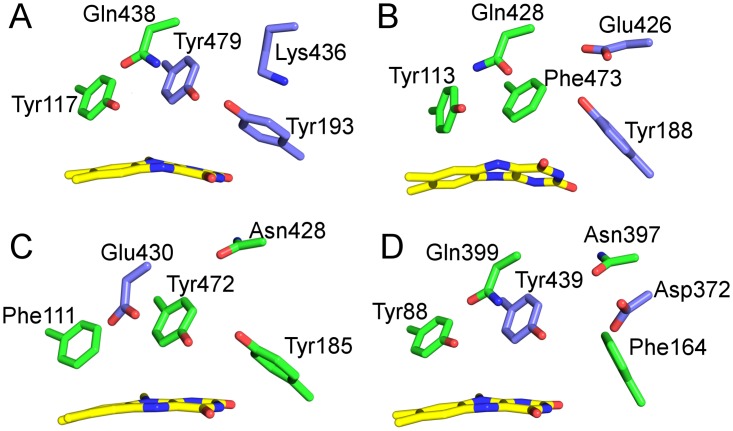
Fig 1. Active site composition of types I-IV (panel A to D) of BBE-like enzymes.
The isoalloxazine ring is shown in yellow. Residues forming the active site are shown in green and residues involved in proton abstraction during catalysis are shown in violet. A: Type I: Tyr117 and Gln438 are engaged in a hydrogen bond. Tyr193 acts as catalytic base, it is stabilized in the deprotonated state by Tyr479 and Lys436 (PDB entry 4UD8). B: Type II. Tyr113 and Gln428 are engaged in a hydrogen bond. Tyr188 putatively acts as catalytic base after de-protonation by Glu426 (PDB entry 5D79). C: Type III: Glu430 putatively acts as catalytic base in the active site. The involvement of Tyr472 and Tyr185 is conceivable. A homology model of Q9SA88 based on 4UD8 and prepared with YASARA was used for visualization [14]. D: Type IV: Tyr88 and Gln399 are engaged in a hydrogen bond, Tyr439 acts as catalytic base after de-protonation by Asp372 via a water molecule (PDB entry 4PWC).