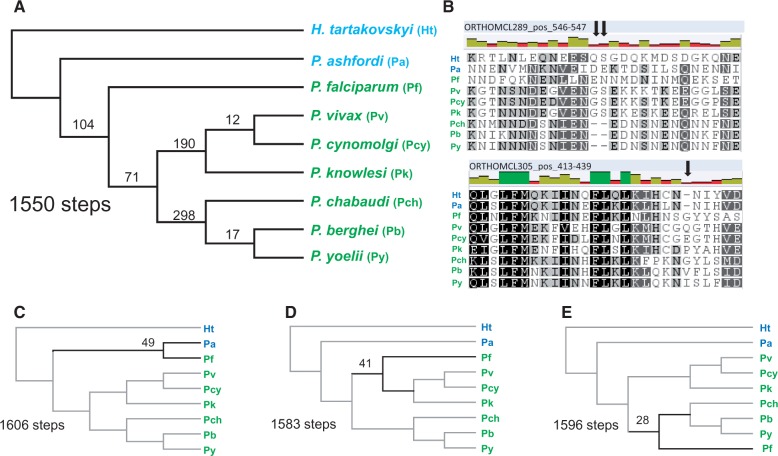
Fig. 5.—
Maximum parsimony tree of 1,116 phylogenetic informative indels of hemosporidian parasites. The tree requiring the lowest number of steps (A) is identical to the tree obtained from sequence-based analyses of amino acids shown in figure 3. (B) Two examples of indels (indicated with arrows) identified within GBLOCKs. The numbers of steps are substantially higher for trees (C) grouping Plasmodium falciparum with the bird parasite Plasmodium ashfordi, (D) grouping P. falciparum with the Plasmodium vivax group, and (E) grouping P. falciparum with Plasmodium parasites infecting rodents. The numbers of indels uniquely shared within clades are shown to the left of the nodes in (A). In (C–E), these numbers indicate the number of indels in conflict with the shortest tree (A). The topology differences between tree (A) and trees (C–E) are indicated by thick branches.