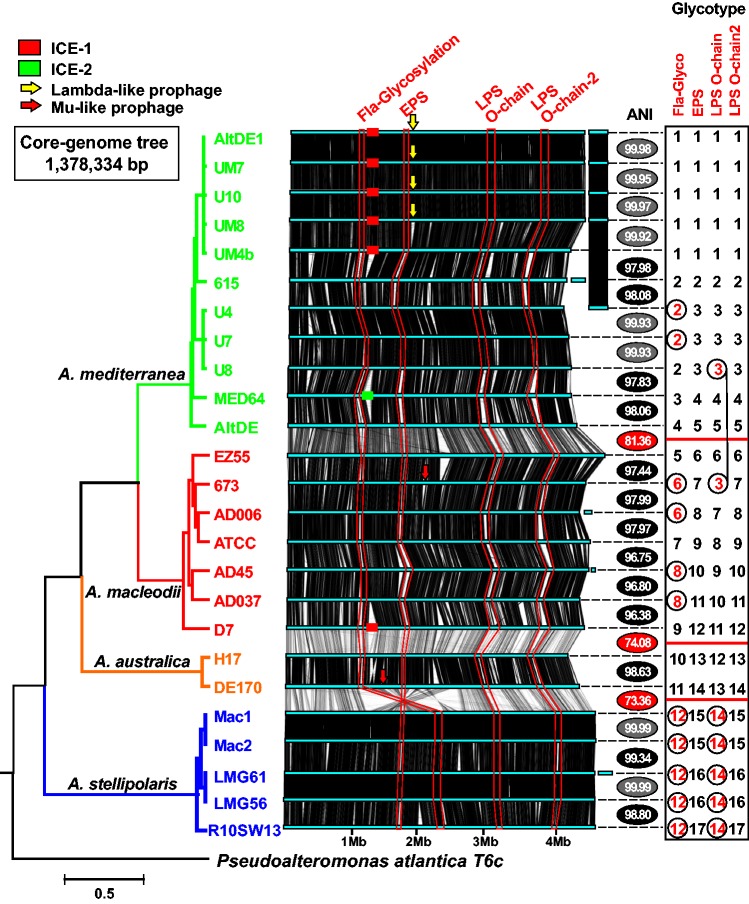
Fig. 1.—
Phylogenomic tree and whole-genome alignment of Alteromonas strains. The genomes have been linearized for the sake of simplicity and are arranged by a phylogenomic tree constructed using a concatenation of the core genome (1.38 Mb). Synteny is indicated by vertical lines connecting the linearized genomes. Plasmids appear at the right hand side. Color of the tree branches indicates members of the same species. Replacement fGIs have been connected by red lines and identified by the inferred function at the top. Arrows show location of phages inserted within the genomes and Integrative and Conjugative Elements (ICEs) are indicated with rectangles, same color indicates same version of the genomic element. The ANI value is intercalated between each genome and the one below (next in the tree). The ANI values with a gray background are between strains belonging to the same clonal frame (CF), black background members of the same species but different CF and red background strains of different species. The panel on the right indicates the type of each replacement fGI present in the corresponding genome. Different numbers correspond to the different versions of each replacement fGI. The combination of numbers for each strain provides a glycotype numerical code. Exchanges between clonal frames or species, i.e., identical or very similar version of the gene cluster in different genomic backgrounds, are highlighted in red.