Fig. 2.
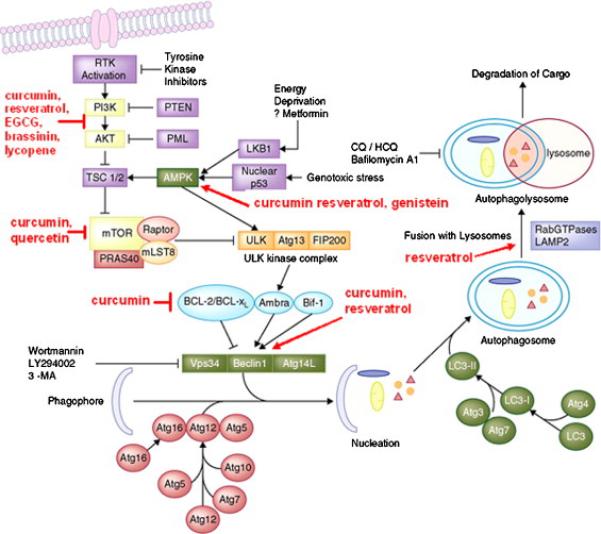
Major pathways of autophagy and natural compounds that inhibit these pathways. Autophagy inducers such as starvation (which may occur during hypoxic conditions) modulate the activity of the phagophore, consisting of the Atg1/unc-51-like kinase (ULK) complex, Beclin 1/PI3K complex, ubiquitin-like proteins (several Atg proteins), and proteins that mediate fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes. Phagophore formation could be blocked with PI3K inhibitors. Autophagy induction involves budding of autophagosomes from the ER membranes, and inhibits interaction of TORC1 with the ULK1/2 complex. The latter regulates the activity of Beclin 1/class III PI3K complex. Beclin 1 interacts with factors that modulate its binding to Vps34, the catalytic unit of the PI3K, whose lipid kinase activity is essential for autophagy. This step could also be pharmacologically blocked. Fully mature autophagosomes can fuse with endosomes to form amphisomes. Autophagosomes or amphisomes fuse their external membranes with those from acidic lysosomes to acquire hydrolytic activity, degrade their cargo, and recycle essential biomolecules to the cytoplasm. Both fusion and degradation could also be inhibited by a variety of compounds, suggesting that autophagy would be a viable target in early stages of carcinogenesis [705].
