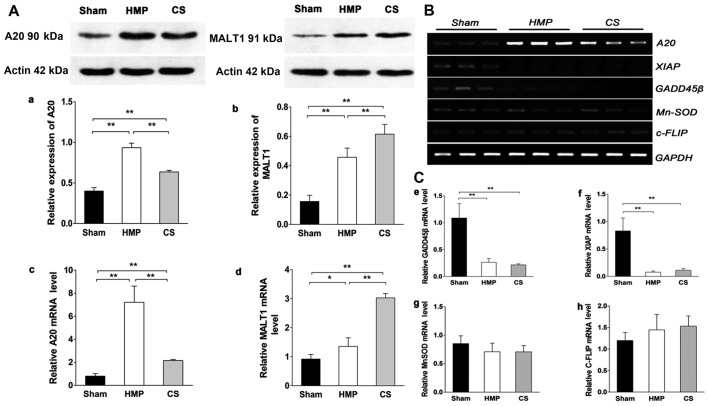
Figure 1.
(A) A20 and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1 (MALT1) expression in the three groups were analyzed by western blot analysis and RT-qPCR. Representative blots are shown. Western blot analysis of (a) A20 and (b) MALT1 protein. β-actin was used as the control. RT-qPCR analysis of (c) A20 and (d) MALT1 mRNA levels. Graphs represent the statistical analysis of relative A20 mRNA levels after normalization against β-actin. In the hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) group, A20 expression was increased compared with that in the cold storage (CS) and sham groups (both **P<0.01). By contrast, MALT1 expression was reduced compared with that in the CS group (**P<0.01). Results represent the means ± SD of three experiments, *P<0.05. (B and C) In the HMP group, the expression of A20, but not of other nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) target genes was significantly increased compared with the levels in the CS group. Levels of particular transcripts were quantified by real-time PCR using gene-specific primers. The amount of each target transcript was normalized against the levels of GAPDH transcript. (B) The mRNA expression of A20, XIAP, GADD45β, MnSOD and c-FLIP was examined in renal tissue. After PCR amplification, the products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. (C-e-g) Compared with the sham group, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45β (GADD45β) were marginally or poorly induced (all **P<0.01), whereas manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) levels were slightly lower in both the HMP and CS groups compared with those in the sham group (both P>0.05). (h) Both the HMP and CS groups showed increased expression of cellular FLICE-inhibitory proteins (c-FLIP) compared with that in the sham group, although there were no significant differences among the three groups. Data represent the means ± SD of three experiments.