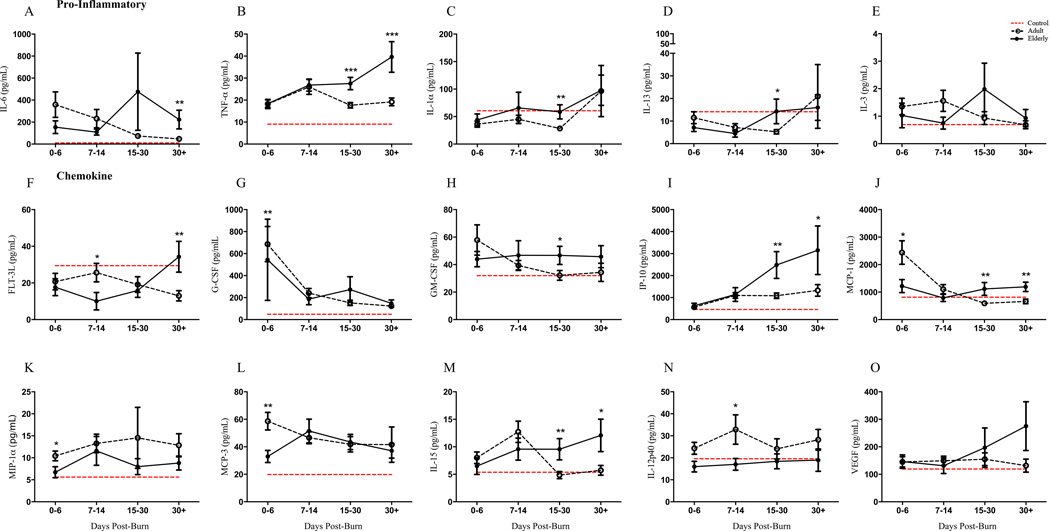
Figure 2.
Plasma cytokine profiling of healthy controls (n = 10), adult (n = 94) and elderly (n = 36) groups over the course of hospital stay (0–6, 7–14, 15–30, 30+ days post burn) showed dramatic alterations relative to healthy controls. The emergence of a delayed immune response in the older group becomes apparent beyond the second week after injury. Comparing both burn groups, pro-inflammatory cytokines were increased in elderly beyond 14-days after injury for IL-6 (A), TNF-α (B), IL-1α (C), IL-13 (D) and IL-3 (E). FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (FLT-3L) (F), Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) (G), Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (H), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10) (I) and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) (J) showed similar delayed upregulation. Other significant alterations were observed in MIP-1α (K), MCP-3 (L), IL-15 (M), IL-12p40 (N). Dashed red lines represent healthy control mean values and data is represented as mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 relative to adult burn group.