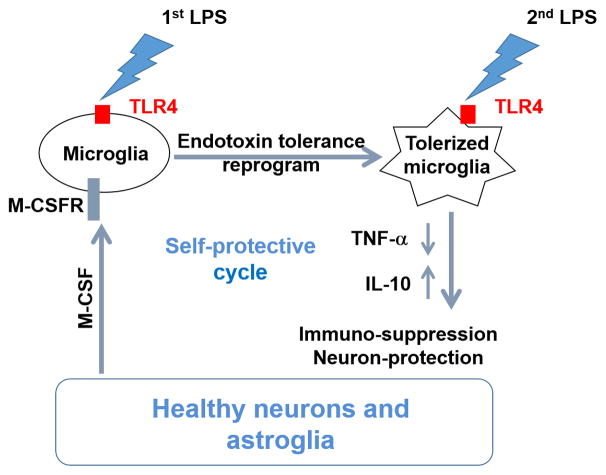
Figure 7. Neurons and astroglia govern microglial ET through M-CSFR-mediated ERK1/2 activation to prevent inflammation-induced neuronal damages.
Under endotoxin challenge, resting microglia could transform into tolerant phenotype where they produce less pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α when encountered a new LPS stimulation. Different from peripheral macrophages, microglia form endotoxin tolerance via a non-cell-autonomous mechanism. Microglia lose their endotoxin tolerance capacity in the absence of neurons and astroglia. The tolerant microglia occur at early stage of neuroinflammation; however they become non-tolerant at later stage of neuroinflammation when neurons and astroglia are injured. M-CSF secreted by neurons and astroglia acts on M-CSFR on microglia to modulate microglia endotoxin tolerance through downstream intracellular ERK1/2 signals.