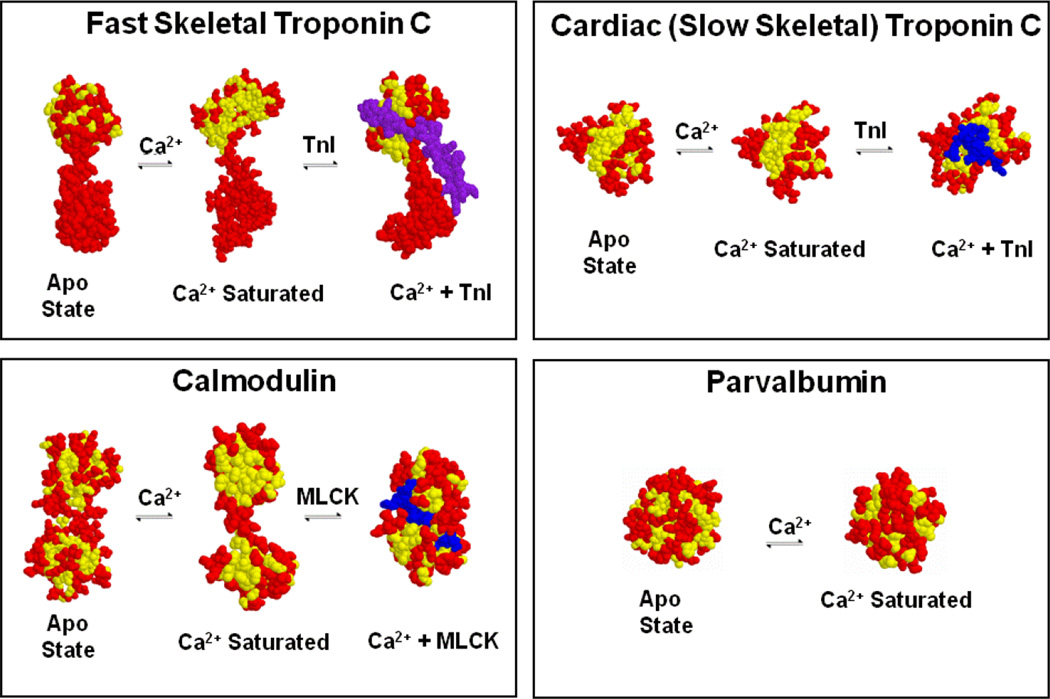
Figure 2. Ca2+-dependent switches and buffers in muscle.
Unlike parvalbumin, TnC and CaM expose a hydrophobic “pocket” upon Ca2+ binding that is then utilized to bind target proteins, TnI in the case of TnC and as an example, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) for CaM. Only the regulatroy, N-terminal domain is depicted for TnC. Yellow amino acids are shown in yellow, whereas all other amino acids are shown in red with the target in blue.