Fig. 3.
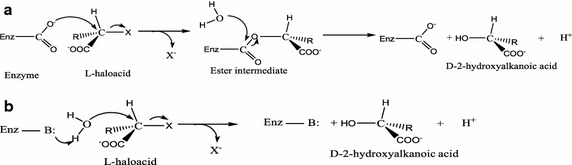
Proposed catalytic reaction mechanisms for l-2-haloacids dehalogenases. a Attack on the C2 of the substrate by a dehalogenase side-chain carboxyl to produce an ester intermediate with subsequent attack by a water molecule on the intermediate to produce the corresponding hydroxyacid with the opposite stereo-configuration. b Water is activated by a basic residue and attacks the substrate to produce the hydroxyacid with simultaneous release of halide ion.
Adapted from Kurihara et al. (1995)
