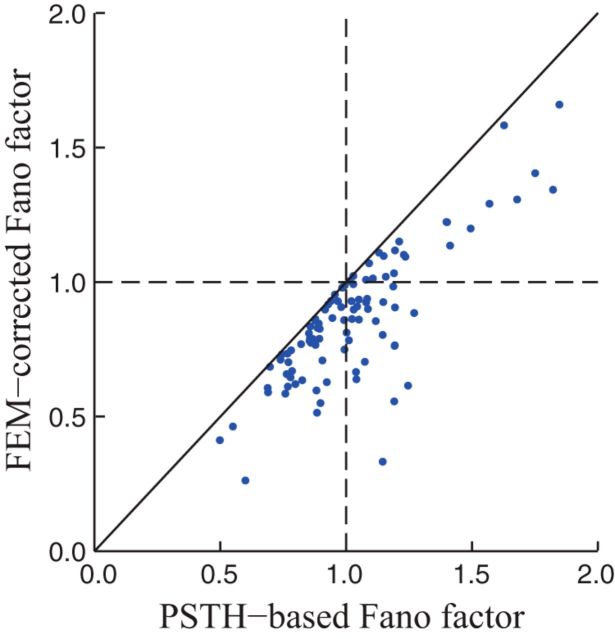
Figure 7.
FEM-induced overestimates of FFs. Comparison of FF estimates using FEM-corrected methods (vertical axis) and standard methods that treat all across-trial variability as noise (i.e., “PSTH-based” estimates; horizontal axis). The effects of FEMs on FF estimates were typically fairly modest (median overestimate of 1.15-fold when ignoring FEMs), but were in some cases fairly dramatic. Overall, when ignoring FEMs, estimated FF values were not significantly different from 1 (median = 1.0, p = 0.84; Wilcoxon signed-rank test). After correcting for FEMs, however, they were significantly <1 (median = 0.86, p = 1.3 × 10−7). Geometric mean FFs were 1.0 and 0.83 without and with FEM corrections, respectively.