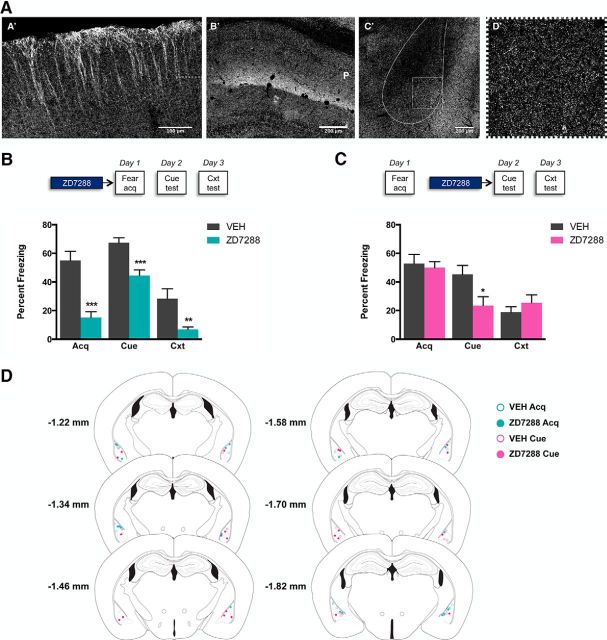
Figure 3.
A, Immunohistochemical staining for Hcn1 reveals dense localization in distal cortical dendrites (A′; dashed line marks separation between layer I/II and layer III) and hippocampal CA1 stratum lacunosum moleculare (B′; P marks the location of the pyramidal cell layer). Hcn1 immunolocalization is evident in the BLA (C′; outlined), with higher magnification of the expected punctate labeling in the BLA (D′; boxed). B, Behavioral pharmacology to examine the role of Hcn channels in the BLA on cued and contextual fear acquisition. Top, Drug administration time course. Bottom, Microinjection of the Hcn channel antagonist ZD7288 (0.3 μg/0.5 μl/side) into the BLA 30 min before cued-fear training impairs fear acquisition in Context A (Acq), cued fear expression 24 h later in Context B (Cue), and contextual fear expression 48 h later in Context A (Cxt). C, Behavioral pharmacology to examine the role of Hcn channels in the BLA on cued and contextual fear expression. Top, Drug administration time course. Bottom, Microinjection of the Hcn channel antagonist ZD7288 (0.3 μg/0.5 μl/side) into the BLA 30 min before cued-fear testing impairs cued fear expression in Context B (Cue), but does not affect contextual fear expression 48 h later in Context A (Cxt). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. n = 9–10/group. D, Summary of cannula tip placements in the BLA in mice treated with vehicle (VEH) or Hcn channel antagonist (ZD7288) (illustration of coronal brain sections from Paxinos and Watson, 1996).