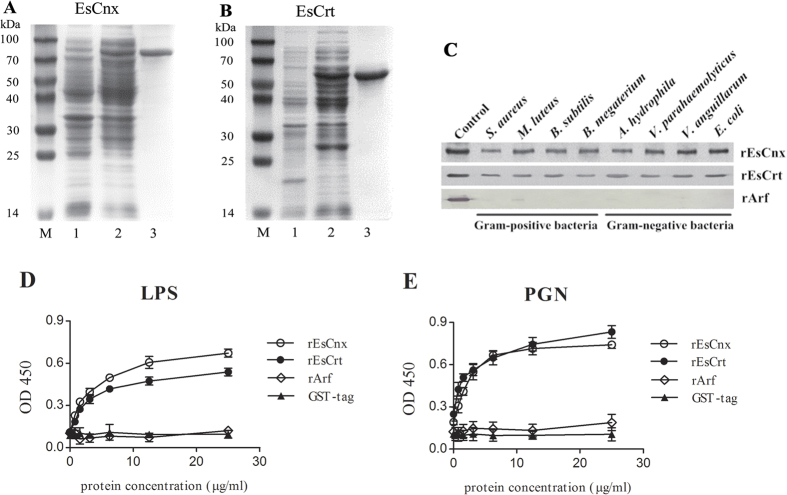
Figure 5.
SDS-PAGE analysis of rEsCnx (A) and rEsCrt (B). Lane M: protein molecular weight standards (kDa); lane A1: negative control for rEsCnx (without induction); lane A2: IPTG-induced rEsCnx; lane A3: purified rEsCnx; lane B1: negative control for rEsCrt (without induction); lane B2: IPTG-induced rEsCrt; and lane B3: purified rEsCrt. (C) Direct binding of rEsCnx and rEsCrt proteins to microorganisms (S. aureus, M. luteus, B. subtilis, B. megaterium, A. hydrophila, V. parahaemolyticus, V. anguillarum, and E. coli). The microorganisms were incubated with rEsCnx or rEsCrt and then washed four times with TBS. ELISA assay was employed to detect the binding of rEsCnx (D) and rEsCrt (E) to LPS and PGN using antiserum against rEsCnx and rEsCrt. All assays were repeated three times.