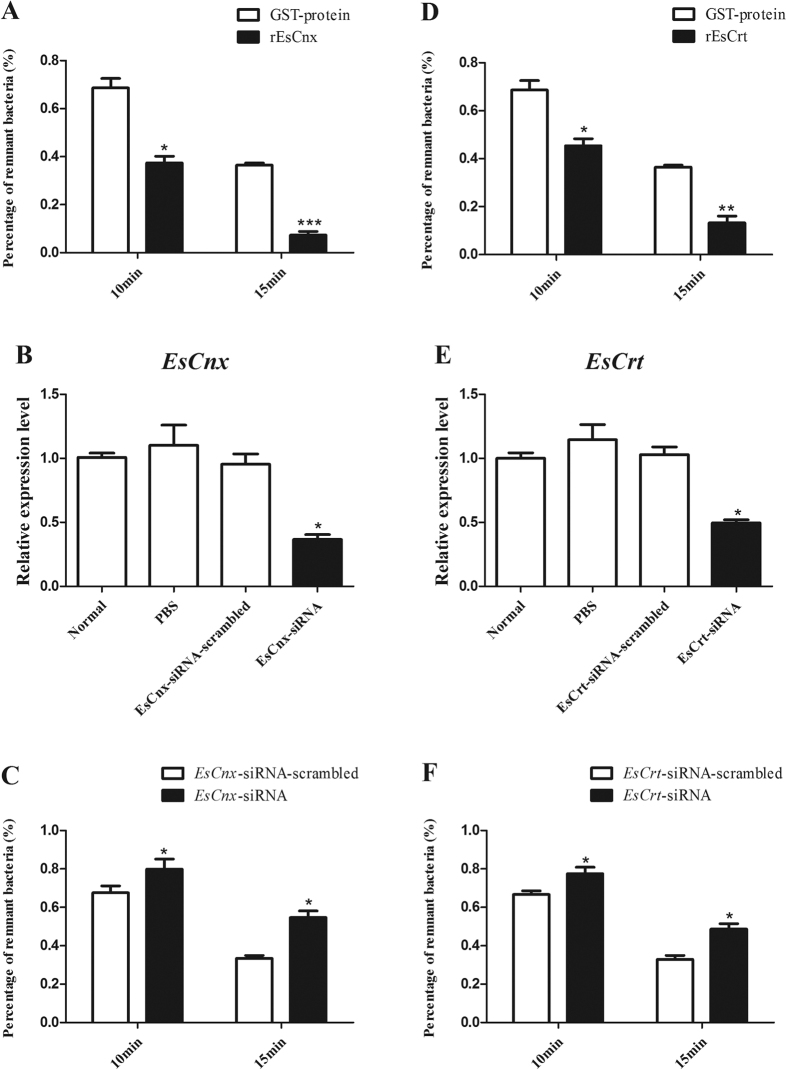
Figure 6.
Effect of rEsCnx and rEsCrt in V. parahaemolyticus clearance activities in crab. rEsCnx (A) or rEsCrt (D) enhanced the clearance of V. parahaemolyticus in vivo. V. parahaemolyticus clearance assay was conducted by pre-coating the injected bacteria with rEsCnx, rEsCrt, or GST-tag protein. The number of remnant bacteria was counted at 2, 10, or 15 min post-injection. The percentage of remnant bacteria was calculated as follows: percentage of remnant bacteria = (number of bacteria at 10 min or 15 min/number of bacteria at 2 min) × 100. RNAi of EsCnx (B) or EsCrt (E) suppressed bacterial clearance in hemocytes. The mRNA transcription level of EsCnx 24 h after injection of EsCnx-siRNA or EsCnx-siRNA-scrambled, as revealed by qRT-PCR analysis. The mRNA transcription level of EsCrt 24 h after injection of EsCrt-siRNA or EsCrt-siRNA-scrambled was revealed by qRT-PCR. The clearance rate of V. parahaemolyticus in crabs was impaired by silencing EsCnx (C) or EsCrt (F) through RNAi. Two groups of crabs were injected with EsCnx-siRNA or EsCrt-siRNA-scrambled (control), and clearance assay was conducted 24 h post-injection.