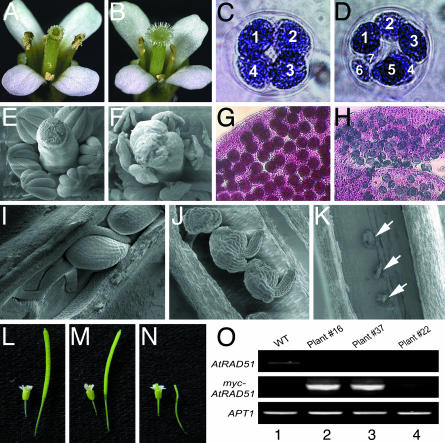
Fig. 2.
Phenotypes of wild-type (A, C, E, G, I, and L), atrad51-1 (B, D, F, H, J, K, and N), and atrad51-1/atrad51-1 35S::MYC::AtRAD51 transgenic plants (M). Shown are opened flowers (A and B), stamens and carpels dissected from unopened flowers (E and F), tetrad (C and D) with numbered microspores, pollen grain (G and H), ovule (I–K; arrows point at aborted ovules), and young siliques (L and N). Two independent 35S::MYC::AtRAD51 transgenic lines (plants 16 and 37) produced siliques (M) that were similar in size to the wild-type ones (L). RT-PCR analysis of these two lines and another sterile transgenic line was performed and shown in O. Lanes: 1, wild type; 2, T1 transgenic plant 16; 3, T1 transgenic plant 37; 4, T1 transgenic plant 22. APT1 expression was determined as a positive control.