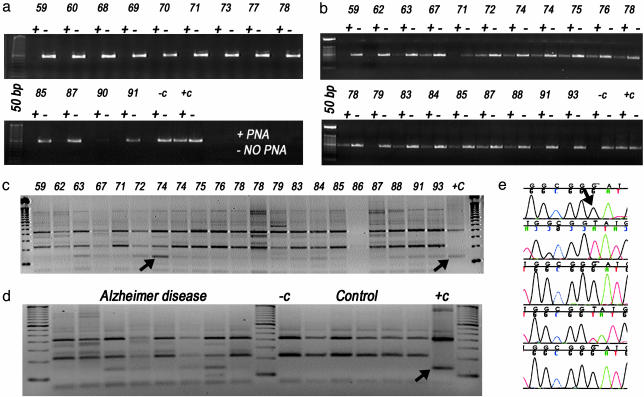
Fig. 2.
PNA-clamping PCR assay for T414G mtDNA mutation in AD and control brains. (a and b) Agarose gel results of controls (a) or AD patients (b). The individual samples in a and b are identified by the age of the subject. Two PCRs are shown for each subject, one in the absence (-) and the other in the presence (+) of a PNA encompassing the 414 wild-type base, which suppresses amplification of the wild-type mtDNA. (c and d) FokI digestion of the PNA-clamping PCR products was used to confirm the presence of the T414G mutation from AD brains (c) and from AD and control brains run into same gel for comparison (d). Lanes in c are labeled with age of AD patients. -c, the FokI digestion result from the PCR product from wild-type plasmid; +c, the result from a T414G mutant plasmid. The arrow indicates the T414G FokI product. (e) Sequence analysis of CR fragments from a 74-year-old subject. The 414 region was PNA-clamping PCR-amplified, the resulting fragments were reamplified without PNA, and the final fragments were cloned and sequenced. The mutant nucleotide G (indicated with an arrow) is seen in three of five clones.