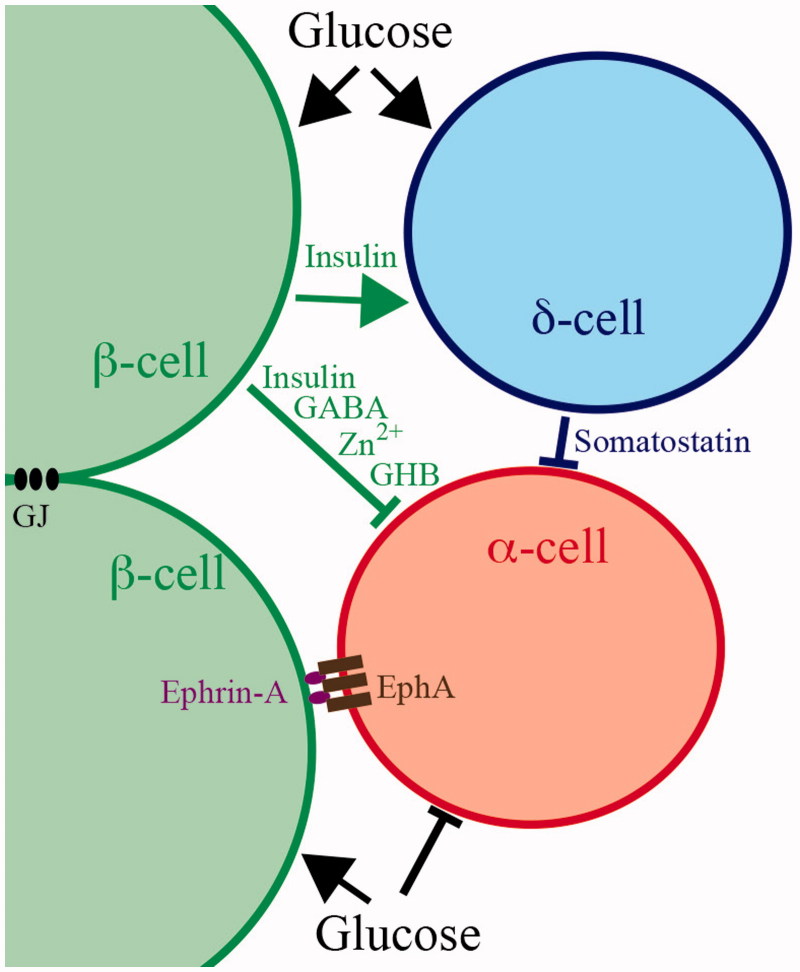
Figure 2. Models for local glucose regulation of glucagon secretion within pancreatic islets. Only the β-cells are electrically coupled by gap junctions (GJ). When stimulated by glucose they release insulin, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), Zn2+, or γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), which have been implicated to mediate inhibition of glucagon secretion from the α-cells. β-Cell-mediated inhibition of the α-cells could also involve juxtacrine ephrin-A–EphA forward signalling. The δ-cells are stimulated by glucose and probably by insulin to release somatostatin that inhibits glucagon release from the α-cells. In addition, glucose has direct inhibitory effects on glucagon release by? -cell-intrinsic mechanisms.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.