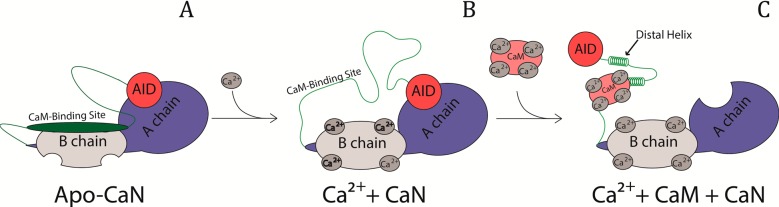
Figure 1.
Activation of calcineurin by calmodulin. (A) The CaM-binding site is located on the regulatory domain (RD), which interacts with the A chain–B chain interface in the absence of Ca2+. (B) The RD is released when the B chain of CaN binds Ca2+. (C) When Ca2+/CaM binds to the CaM-binding site of CaN, the distal helix folds onto CaM, and the AID dissociates from the active site, fully activating the phosphatase.