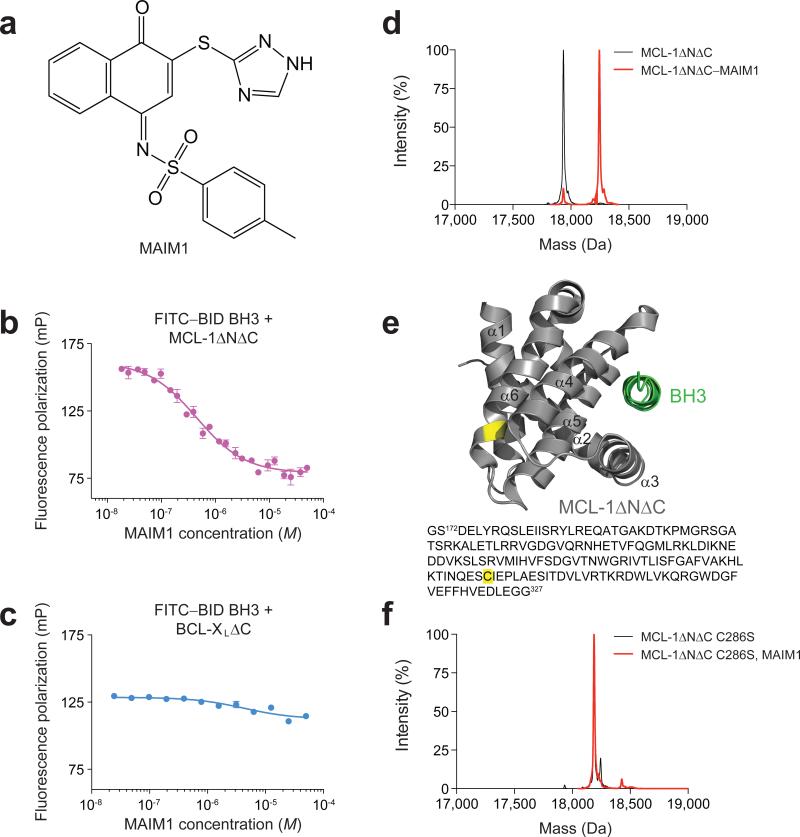
Figure 1. Selective inhibition of MCL-1ΔNΔC binding activity by covalent modification of C286.
(a) Chemical structure of MCL-1 Allosteric Inhibitor Molecule 1 (MAIM1). (b) Fluorescence polarization (FP) competitive binding assay for MAIM1 inhibition (IC50, 450 nM) of the interaction between FITC–BID BH3 (15 nM) and MCL-1ΔNΔC (125 nM). (c) Negative control FP assay for MAIM1, as tested on the binding interaction between FITC–BID BH3 (15 nM) and BCL-XLΔC (125 nM). (d) Intact protein mass spectrometry (MS) of MCL-1ΔNΔC (black, 17937 Da) and MAIM1-derivatized [naphthoquinone tosylimine] MCL-1ΔNΔC (red, 18247 Da). (e) MAIM1 derivatization of MCL-1ΔNΔC C286 (yellow), as determined by MS/MS analysis. The location of the BH3-binding groove is demonstrated by MCL-1 SAHBD (green) (PDB ID 3MK8 (ref 12)). (f) Intact protein MS of MCL-1ΔNΔC C286S alone (black, 18191 Da) and in the presence of MAIM1 (red, 18191 Da). Of note, the peaks are overlapping (red trace obscures underlying black trace). Error bars are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 technical replicates each for FP assays).