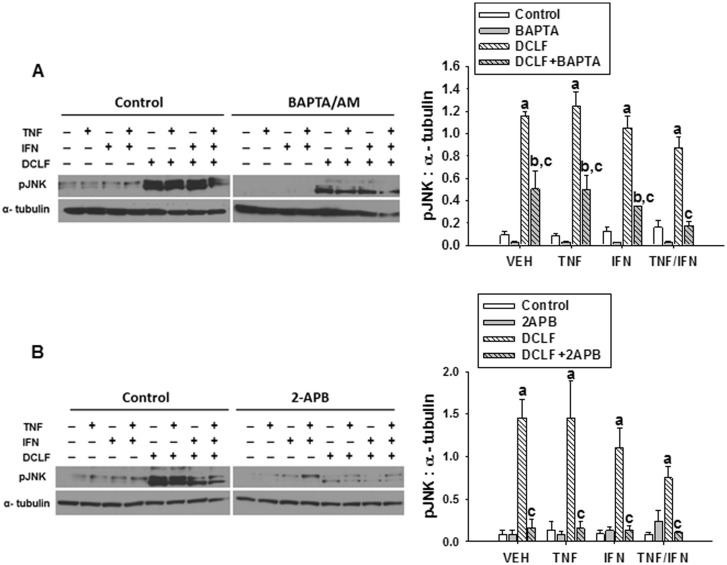
FIG. 5.
Ca++ contributes to DCLF-mediated JNK activation. HepG2 cells were treated with VEH (0.1% DMSO), (A) BAPTA/AM (10 μM, 4 h before addition of DCLF/cytokines) or (B) 2-APB (100 μM, simultaneous addition with DCLF/cytokines) and treated with sterile water (Control) or DCLF (250 µM) alone or in combination with TNF (10 ng/ml) and/or IFN (10 ng/ml). Proteins were collected 18 h after drug treatment. pJNK and α-tubulin levels were detected via western analysis. a, significantly different from Control group within a cytokine treatment. b, significantly different from BAPTA/AM (A) or 2-APB (B) within a cytokine treatment group. c, significantly different from DCLF within a cytokine treatment. Western analysis of proteins from cells treated with and without BAPTA/AM or 2-APB was performed simultaneously. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of at least 3 experiments. Abbreviations: VEH, vehicle; DCLF, diclofenac; pJNK, phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase; BAPTA/AM, acetoxymethyl-1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid; APB, aminophenoxydiphenyl borate.