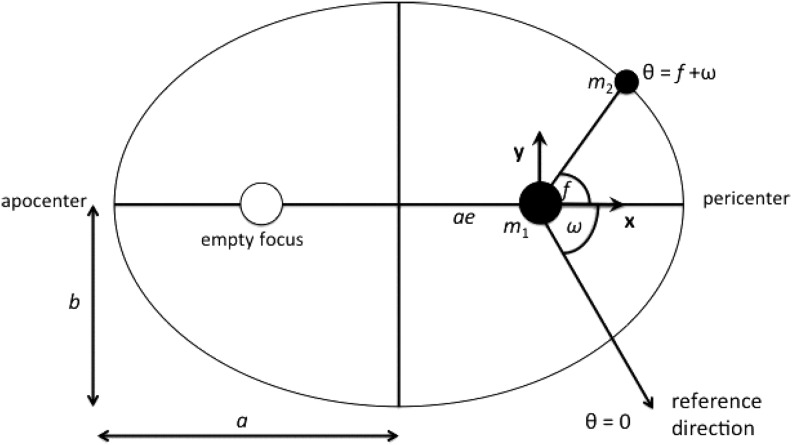
FIG. 1.
Geometry of the elliptical orbit of a body of mass m2 around m1. The ellipse has semimajor axis a, semiminor axis b, eccentricity e, and longitude of pericenter ω. The true anomaly f denotes the angle subtended by an imaginary line connecting m1 with the location of m2 in its orbit and one connecting m1 with pericenter (the point of closest approach to m1). This assumes that m1 >> m2.