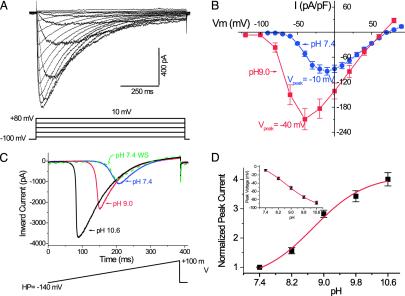
Fig. 2.
NaVBP is a voltage-gated Na+ channel modulated by extracellular alkaline pH. (A) Representative traces (Upper) of INavBP activated by the voltage protocol shown. Holding potential (VHP =–100 mV). The cell was bathed in 10 mM Ca2+ external solution (140 mM Na+ /10 mM Ca2+/5mMK+ pipette; 147 mM Cs+ /8mMNa+ ; see Materials and Methods). (B) Averaged peak current–voltage (I–V) relation of NaVBP in standard bath solution at pH 7.4 (blue, n = 19, VHP = –100 mV), and pH 9.0 (red, n = 11, VHP =–130 mV), normalized by cell capacitance (pF). (C) Increasing pHo reversibly potentiated INavBP generated by a ramp protocol (–140 mV to + 100 mV in 380 ms, VHP =–140 mV). (D) pHo-dependent changes on the normalized amplitude of the peak inward current (n = 9; ± SEM). The pHo-dependent shifts of the peak voltage is plotted (Inset).