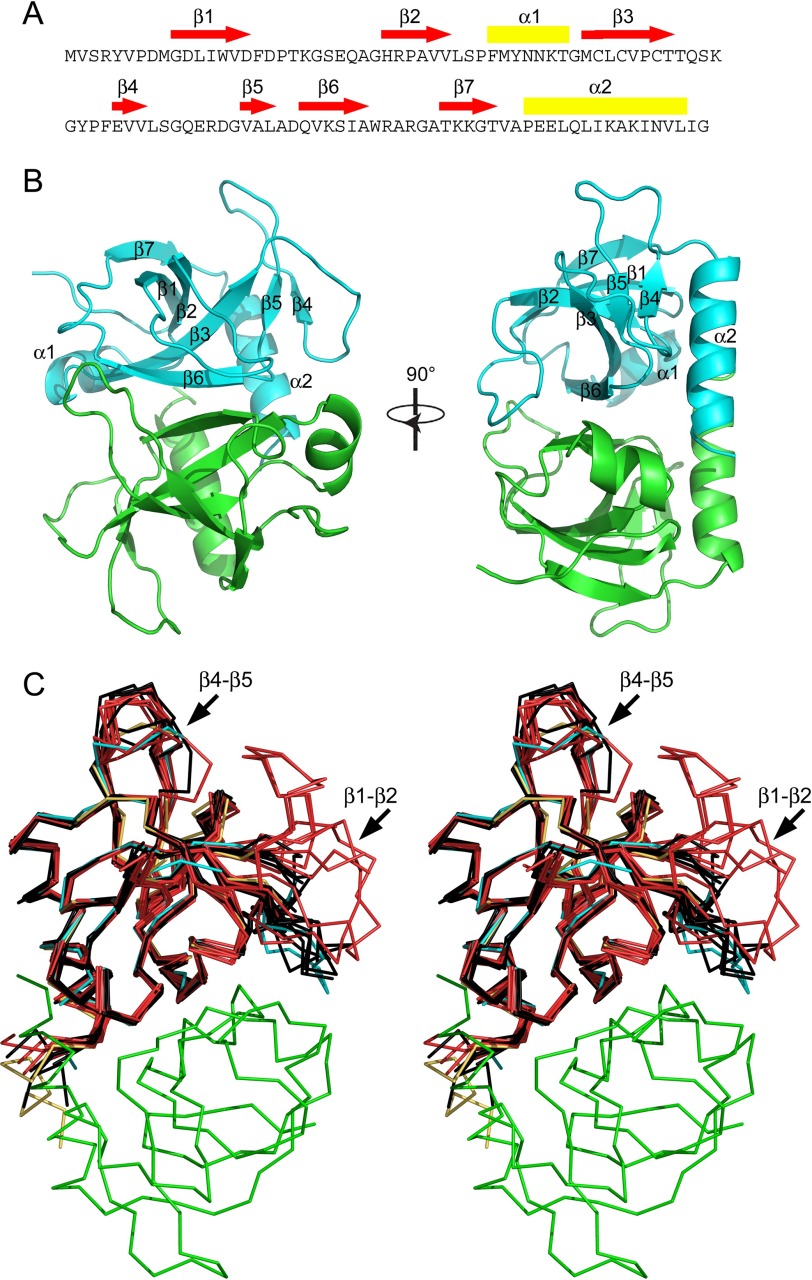
FIGURE 1.
Structure of wild type EcMazF and EcMazFE24A. A, amino acid sequence of EcMazF with the different secondary structure elements identified. Red arrows correspond to β-strands, and yellow rectangles correspond to α-helices. B, stereo view of the EcMazF dimer (PDB entry 5CR2) with each secondary structure element as well as the N and C termini labeled in one monomer. C, Cα trace of the EcMazF dimer of the d(AUACAUA) complex (PDB entry 5CR2) with one monomer in cyan and the other in green in two perpendicular orientations. Superimposed are all crystallographically independent monomers of the wild type EcMazF structures (in black) and of the EcMazFE24A structures (in red). One EcMazFE24A monomer of the complex with EcMazE(68–82) is shown in yellow. The position of loops β1-β2 and β4-β5 are indicated.