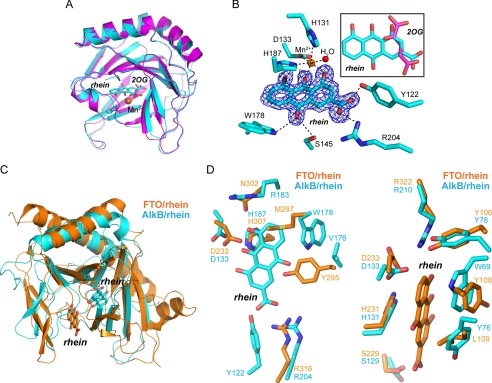
FIGURE 5.
Structural insights into the mode of rhein binding to AlkB. A, structure alignment of the AlkB-rhein (PDB code 4RFR) and 2OG-bound AlkB (PDB code 3I3Q) performed in PyMOL with RMSD = 0.28 Å. The AlkB-rhein structure is colored cyan, AlkB/2OG is magenta, and the oxygen atom is red, respectively. Mn2+ is shown as a sphere and colored orange. Rhein and 2OG are shown as sticks. B, an m|Fo| − D|Fc| map was calculated within the PHENIX program suite after omission of rhein from the complex model and subsequent simulated annealing. The map density is contoured to 3.0 σ. The coordination of Mn2+ by ligands and hydrogen bonding are denoted by dotted dark lines. The map is shown in blue. The superimposition of rhein and 2OG is presented. C, structural superimposition of AlkB-rhein and FTO-rhein complexes performed in PyMOL. The FTO/rhein (PDB code 4IE7) is colored orange. Rhein is shown as sticks. D, zoomed-in view token from C to show the pocket for rhein binding to AlkB and FTO, respectively. Rhein could not bind to FTO similarly to AlkB because of the steric clashes by Tyr295 and Met297 (left panel). A likely binding pocket is observed in AlkB for rhein binding similarly in FTO (right panel).