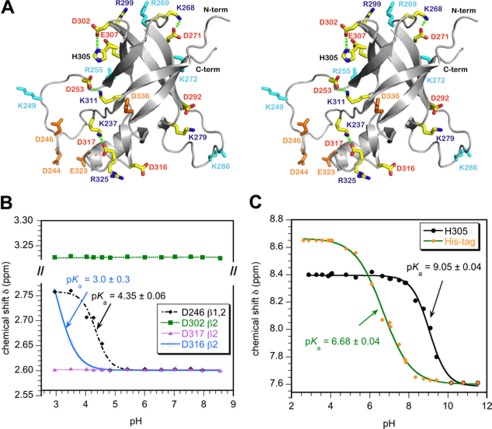
FIGURE 1.
Ion-pair interactions in the I-domain. A, stereo diagram of the I-domain NMR structure showing charged residues. Acidic and basic residues that do not participate in ion pairs are colored orange and cyan, respectively. Residues that participate in ion pairs (Table 1) are labeled red and blue for acidic and basic amino acids, respectively. Hydrogen bonds that link ion pairs in a salt bridge (Asp-302–His-305, Asp-253–Lys-311, Asp-271–Lys-268, Asp-317–Lys-237) are indicated by dashed green lines. B, representative NMR pH titration data for aspartate Hβ protons. Asp-246 is in the disordered D-loop and has a random coil pKa. Asp-316 forms an ion pair with Arg-325 and has the lowest pKa measured in the I-domain. Asp-302 and Asp-317 form hydrogen-bonded salt bridges (Table 1) and do not shift with pH. C, NMR pH titration of histidine Hϵ1 protons. The unresolved resonances from the His6 tag used for purification gave a pKa of 6.7, in agreement with the random coil histidine value (43). By contrast His-305 had a pKa value shifted up by 2.5 pH units, consistent with the residue forming a stabilizing salt bridge with Asp-302.