FIGURE 3.
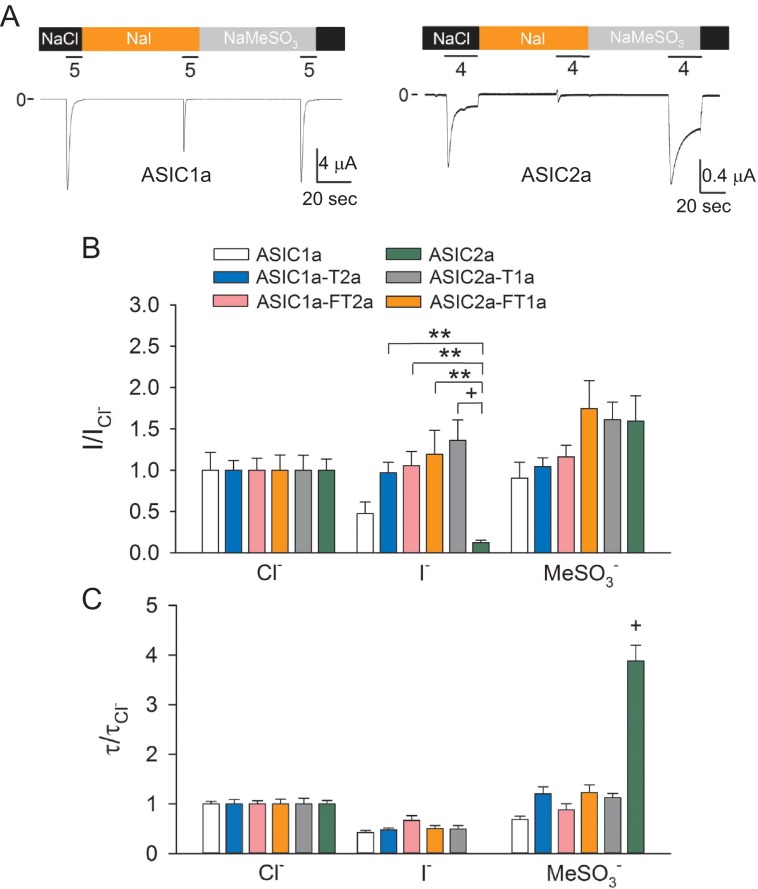
Extracellular anion modulation of ASIC1a, ASIC2a, and finger-thumb chimeras. A, representative recordings of experiments conducted with oocytes expressing ASIC1a and ASIC2a in solutions containing Cl−, MeSO3−, or I−. Whole-cell currents were elicited by a change in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0 (ASIC1a) or 4.0 (ASIC2a). Note that ASIC2a does not response to extracellular acidification in the presence of I−. B, effect of anion substitution on the response to extracellular acidification of ASIC1a, ASIC2a, and chimeras. Whole-cell currents were evoked by a change in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0 (ASIC1a, ASIC1a-F2a, ASIC1a-T2a, and ASIC1a-FT2a) or to 4.0 (ASIC2a, ASIC2a-T1a, and ASIC2a-FT1a). The relative response (I/ICl−) represents the ratio of the pH-elicited peak current to the pH-elicited peak current in Cl−. **, p < 0.01; +, p < 0.001 (n = 10–14) (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test). C, effect of anion substitution on the time constants of desensitization of ASIC1a, ASIC2a, and chimeras. The time constants of desensitization were estimated by fitting the current decay after extracellular acidification to a single exponential function as described under “Experimental Procedures.” For ASIC1a, ASIC1a-F2a, ASIC1a-T2a, and ASIC1a-FT2a, currents were evoked by a drop in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0, whereas for ASIC2a, ASIC2a-T1a, and ASIC2a-FT1a, currents were elicited by a drop in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 4.0. Statistically significant difference with ASIC1a and chimeras is indicated. +, p < 0.001 (n = 10–14) (analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test).