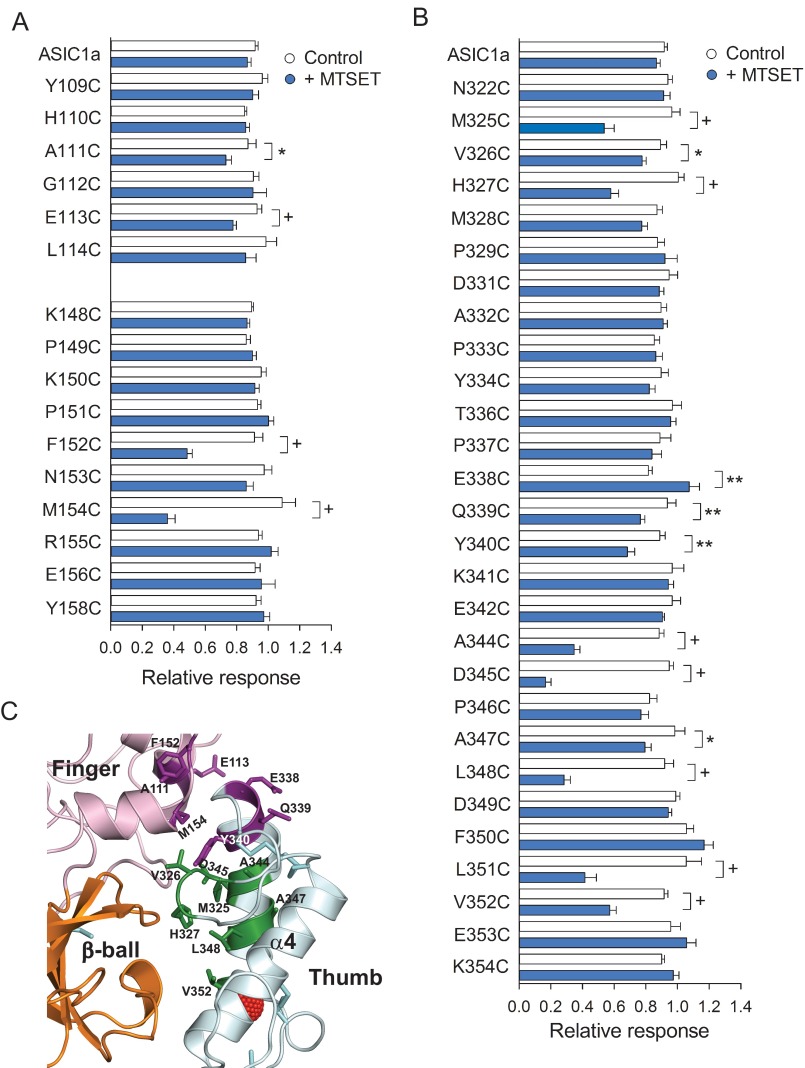
FIGURE 5.
Covalent modification of Cys residues at the finger-thumb and β-ball-thumb interfaces diminishes the response to extracellular acidification. A and B, reactivity toward MTSET of channels bearing Cys substitutions at selected sites in the finger (A) and thumb (B) domains. Whole-cell currents were evoked by a change in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0 before and after MTSET treatment. The relative response represents the ratio of the pH-elicited peak current following MTSET treatment (or control) to the pH-elicited peak current before treatment. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; +, p < 0.001 (n = 9–36) (t test). C, schematic illustrating sites in the finger and thumb domains sensitive to MTSET treatment when mutated to Cys. Disulfide bridges are shown as cyan sticks. Sensitive sites in the finger domain are colored purple. Sensitive sites in the thumb domain colored purple (Glu338, Gln339, and Tyr340) reside near the finger domain, whereas sites colored green (Met325, Val326, His327, Ala344, Asp345, Ala347, Leu348, Leu351, and Val352) reside near the β-ball domain.