Figure 3.
Structural Requirements of HsfA1 and HsfB1 for Synergistic Activation of the pHsp17*-GUS Reporter.
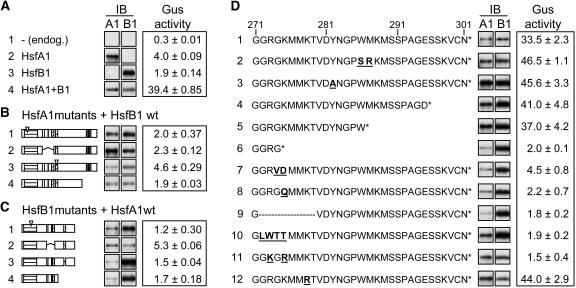
Immunoblots (IB) in (A) to (D) reflect the expression levels of the HSFs. Mutant forms of HsfB1 in the following figures are abbreviated as follows: M4, DNA binding mutant (C1); Δ, mutant with deletion of amino acids 272 to 279 (D9); R, mutant with 272-GRGK>GKGR.
(A) GUS activities measured with the four standard samples (arrows in Figure 1B). Sample 4 transformed with HsfA1 and HsfB1 represents the reference for all samples in (B) to (D).
(B) and (C) GUS activities of samples coexpressing the indicated mutant forms of HsfA1 and wild-type HsfB1 (B) or, vice versa, the wild type of HsfA1 with mutant forms of HsfB1. Block diagrams of HsfA1 and HsfB1 (C) were shown in Figure 1A. For further details about the mutants, see Methods and Supplemental Table S1 online.
(D) Functional dissection of the CTD (amino acids 271 to 301) of HsfB1. Amino acid residues that changed in the mutant forms of HsfB1 are highlighted by underlined boldface letters. All GUS activities were measured by coexpressing HsfA1 and the indicated mutant forms of HsfB1.