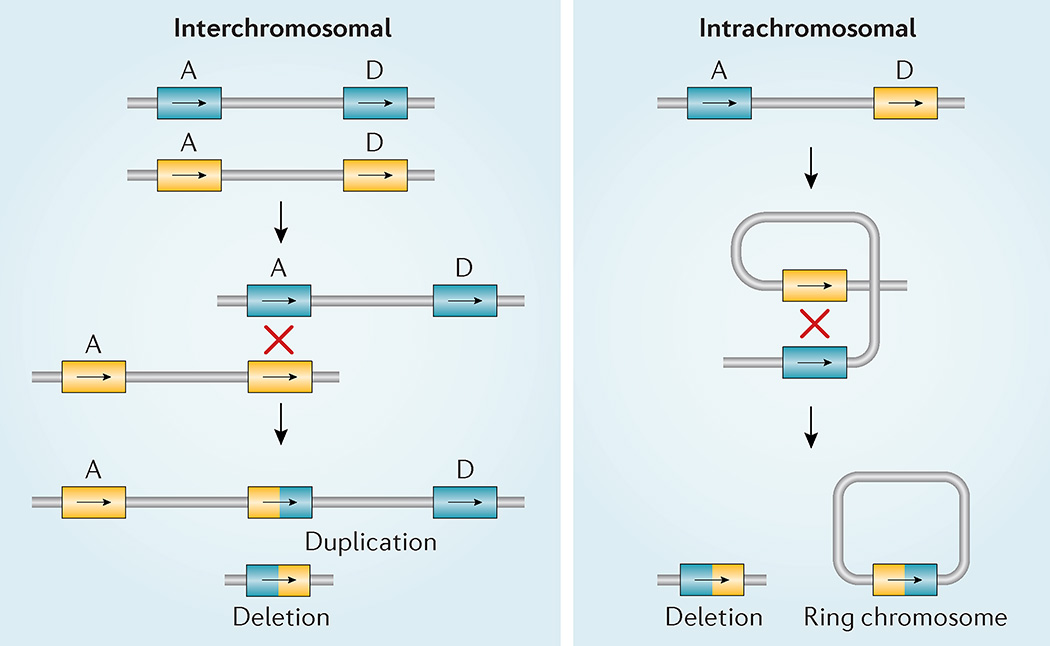
Figure 3. 22q11.2 non-allelic homologous recombination.
Diagram of two different types of meiotic non-allelic homologous recombination events that can occur between low copy repeats on chromosome 22 (LCR22s). Rearrangements between LCR22A and LCR22D are indicated (A and D) on each allele (blue versus yellow). Interchromosomal events (left) occur between paralogous LCR22s (A and D) in two different alleles owing to >99% sequence identity of direct repeats (‘X’ shows the crossover of the two chromosomes). The hybrid LCR22 is shown as half yellow and half blue. This process results in a duplication or deletion of intervening genes in resulting gametes. Intrachromosomal recombination events (right) result from crossing over (indicated by ‘X’) within one allele, resulting in a deletion (left) or a ring chromosome (right); the ring chromosome is not viable.