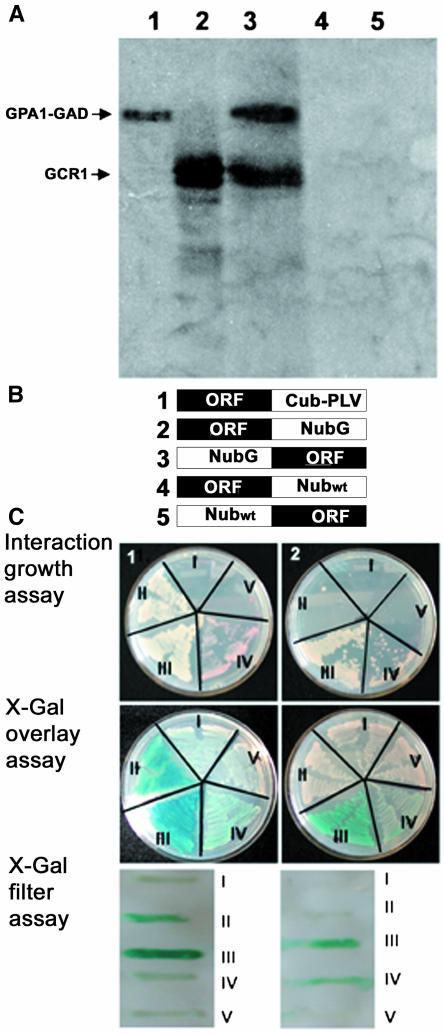
Figure 1.
GCR1 Interacts with GPA1.
(A) GCR1 interacts with GPA1 under in vitro conditions. GPA1 and a putative protein kinase (At5g66890) were prepared with the GAL4 activation domain (GAD) as fusion proteins. GPA1-GAD fusion proteins and GCR1 were synthesized by in vitro transcription/translation in the presence of 35S-Met (lanes 1 and 2). Kinase-GAD fusion protein was in vitro transcribed/translated in the presence of cold Met. GCR1 can be pulled down with GAD antibodies when incubated with GPA1 (lane 3) but not when incubated with the anti-GAD antibodies alone (lane 4) or the putative protein kinase (lane 5).
(B) Constructs used for split ubiquitin assays. Protein fusion with the C-terminal part of ubiquitin followed by PLV (Cub-PLV) was made at the C terminus of the bait protein (1). Protein fusions with the N-terminal part of ubiquitin (Nub) were made either at the C terminus of the prey protein with NubG or Nubwt (2 and 4, respectively) or at the N terminus of the prey protein with NubG or Nubwt (3 and 5, respectively).
(C) GCR1 and GPA1 interact in yeast-based split ubiquitin system. Interaction between GCR1 and GPA1 was determined by growth assay on media lacking His and Ade but containing 200 μM Met, by β-galactosidase activity using X-Gal overlay assay, and by X-Gal filter assay. (1) Interaction assays with GPA1-Cub as bait construct. The constructs were used in the following combinations: (I) GPA1-Cub + GCR1-NubG, (II) GPA1-Cub + NubG-GCR1, (III) GPA1-Cub + GCR1-Nubwt, (IV) GPA1-Cub + Nubwt-GCR1, and (V) GPA1-Cub + GPA1-NubG. GCR1-NubG and NubG-GCR1 were test constructs (I and II). GCR1-Nubwt constructs serve as positive controls (III and IV). The GPA1-NubG construct serves as a negative control (V). GPA1-Cub interacts with GCR1 only when the NubG fusion is at the N terminus of GCR1 (II) and not when the C terminus of GCR1 is fused with NubG (I). (2) Interaction assays with GCR1-Cub as bait construct. The constructs were used in the following combinations: (I) GCR1-Cub + GPA1-NubG, (II) GCR1-Cub + NubG-GPA1, (III) GCR1-Cub + GPA1-Nubwt, (IV) GCR1-Cub + Nubwt-GPA1, and (V) GCR1-Cub + GCR1-NubG. GPA1-NubG and NubG-GPA1 were test constructs (I and II). GPA1-Nubwt constructs serve as positive controls (III and IV). The GCR1-NubG construct serves as a negative control (V). GCR1 fused with Cub at its C terminus fails to interact with GPA1. Growth and β-galactosidase activity tests are positive only for the positive controls (III and IV) that have wild-type ubiquitin fused with GPA1.